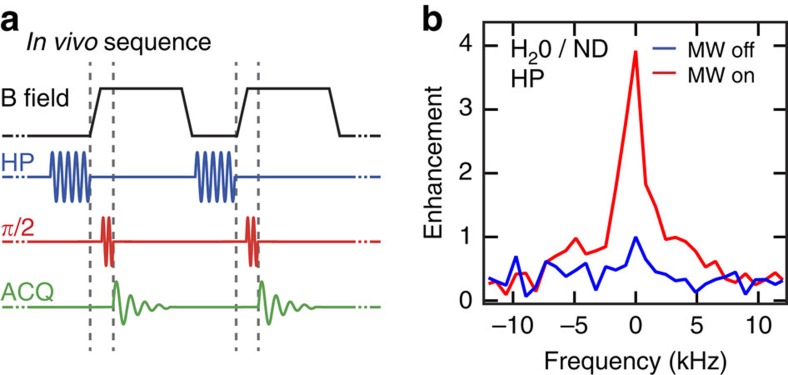
Figure 3. ND hyperpolarization in the precence of water.
(a) The combination of room temperature signal enhancement and long relaxation times opens the possibility of in vivo hyperpolarization using a magnetic field shuttling technique. With the ND agents already administered to the biosystem, hyperpolarization (HP) is performed at low field where microwave heating is reduced. The field is then ramped on a timescale much shorter than T1 to enable imaging and detection of the hyperpolarized ND. Schematic shows a repeated sequence with radio frequency π/2 -pulses and acquisition window (ACQ). (b) Hyperpolarization in the presence of water, mimicking in vivo conditions. Even at the high microwave frequency of 80 GHz, we observe an enhanced signal (red) of approximately four times compared with the thermal polarization (blue).