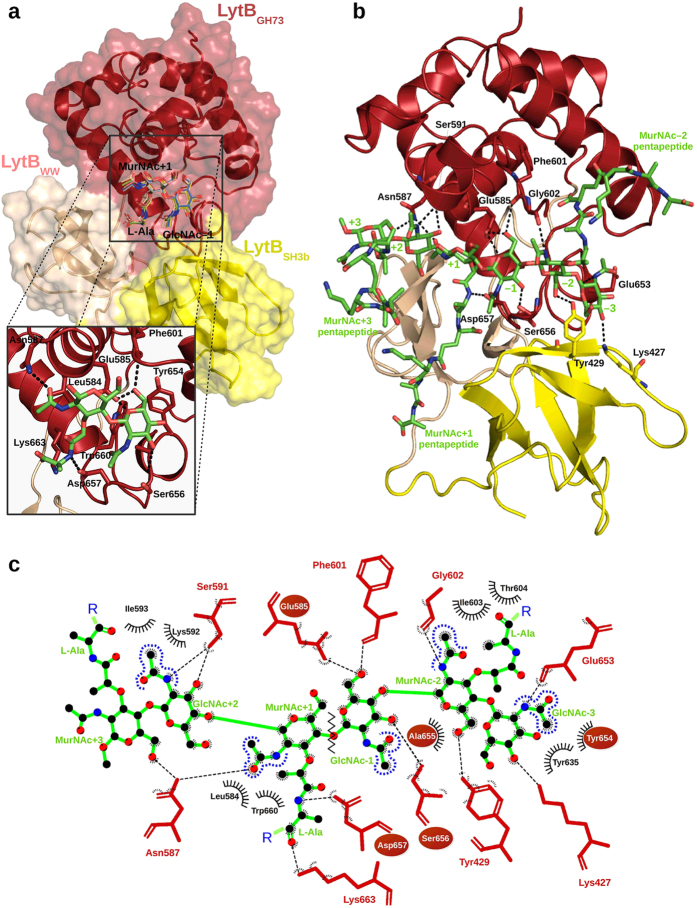
Figure 5. Models of LytBCAT complexes with PG analogues.
(a) Surface representation of the LytBCAT/GlcNAc-MurNAc-L-Ala complex generated by AutoDock 4.2. Saccharide units are docked into +1/−1 subsites of the binding site. The ten lower energy solutions obtained are drawn in line representation. The inset shows the contact network at subsites +1 and −1 for the best docking complex. Dashed lines indicate the hydrogen bonds and the residues involved are shown as red (LytBCAT) or green (ligand) sticks. (b) Putative interactions between the domains of LytBCAT and (GMPP)3 (green sticks) in the computational model created by extending the best docking solution for the LytBCAT/GlcNAc-MurNAc-L-Ala complex. Protein residues involved in hydrogen bond formation are depicted as sticks. (c) Schematic representation of contacts between LytBCAT and (GMPP)3 glycan strand analyzed with LigPlot+ v.1.465. Van der Waals interactions are shown with black arcs. The catalytic Glu585 and the conserved YASD tetrad are highlighted with red ovals, and the zig zag line indicates the scissile bond. The same colour code was used in the whole figure: GlcNAc-MurNAc-L-Ala and (GMPP)3 are depicted in green, whereas LytBGH73, LytBSH3b and LytBWW domains are in red, yellow and salmon, respectively.