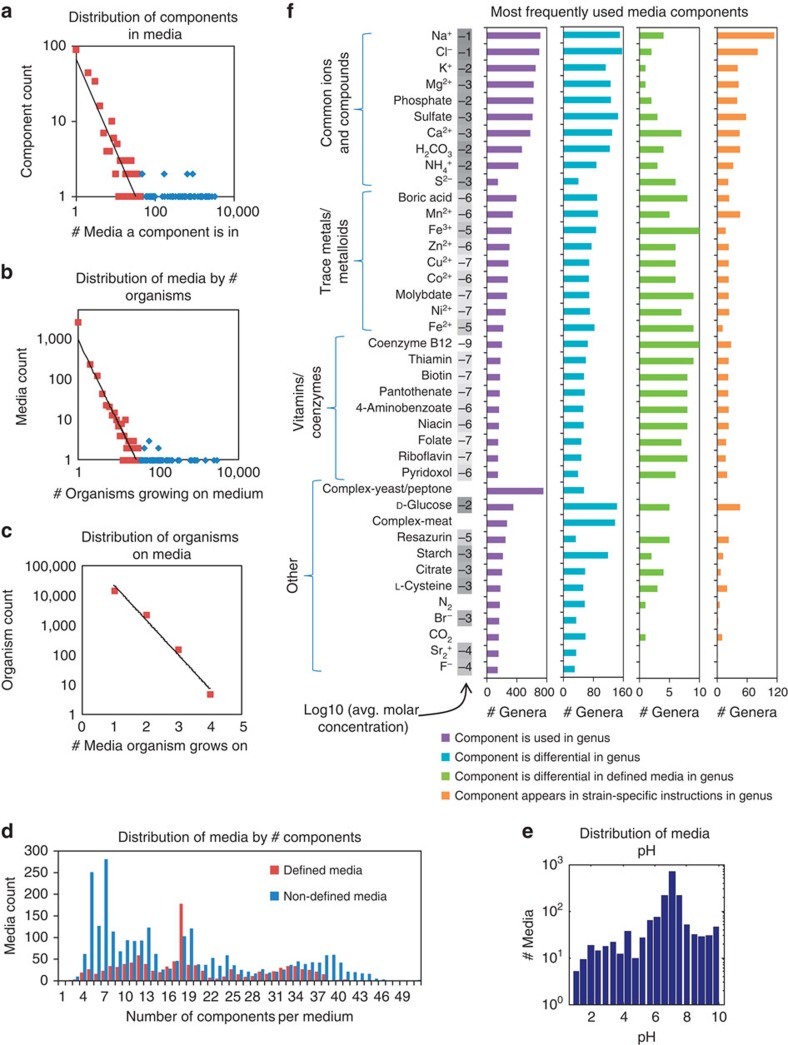
Figure 2. Large-scale properties of known media.
(a) Distributions of components in media. This includes both defined and complex/undefined components, where undefined components are grouped into their complex categories and each category present in a medium is counted as one component. (b) Distributions of media by the number of organisms that grow on them. (c) Distributions of the number of media that organisms grow on. (d) Distribution of media by the number of components within them. (e) Distribution of pH values of known media. Red squares in a and b denote the bins used for the power law fit. (f) The 40 most frequently used media components across genera. Ions listed here were typically added to media as salts, which we assume completely dissociate in solution (for example, MgCl2 becomes Mg2+ and Cl−). Components are broken into four groups: biologically common ions/compounds, trace metals/metalloids, vitamins/coenzymes and other. Within each group, components are listed in order of their frequency of usage across genera, from most to least. Left of the bar graphs is a list of average concentrations of each component in media across KOMODO, listed in units of log10(molar concentration). A component is ‘differential' in a genus if it appears in media for some strains in that genus but not others.