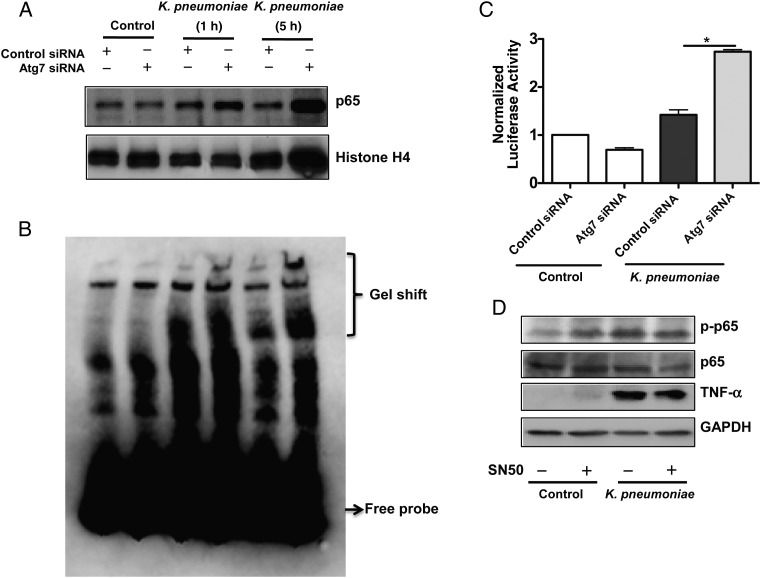
Figure 2.
Nuclear factor (NF) κB translocated into nuclei in autophagy-related gene (Atg) 7–silenced cells. A, NF-κB levels were increased in the Atg7-silencing cells. Cells from the murine alveolar macrophage cell line (MH-S) were transfected with Atg7 small interfering RNA (siRNA) or control (scrambled) siRNA. After 24 hours, the cells were infected with Klebsiella pneumoniae for 1 hour and 5 hours. Nuclear fractions were isolated from cells by a nuclear extraction kit (Thermofisher). B, Electrophoretic mobility shift assay was performed in MH-S cell nuclear extracts using the biotin-labeled probe (Thermofisher), which contains only a single copy of the 21–base pair element. C, Increased luciferase reporter activity of NF-κB in Atg7 siRNA–transfected MH-S cells. MH-S cells were transfected with Atg7 siRNA or control siRNA. After 24 hours, cells were transfected with luciferase reporter NF-κB plasmid. After 24 hours of transfection, cells were infected with K. pneumoniae at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 10:1 for 1 hour. Cell-permeable NF-κB inhibitor (SN50) (1.8 µmol/L) was used to pretreat cells for 0.5 hour before infection. *P < .001 (1-way analysis of variance and Bonferroni selected multiple comparison test). D, Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) α expression was decreased after inhibiting NF-κB with SN50 (1.8 µmol/L). MH-S cells were infected with K. pneumoniae at an MOI of 10:1 for 1 hour. Data were representative of 3 experiments. Abbreviations: +, with; −, without; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase.