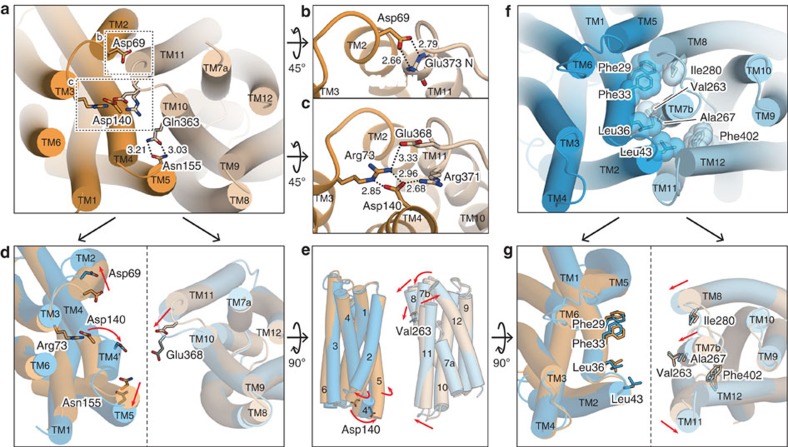
Figure 5. Structures of the intra- and extracellular gates and structural comparison.
(a) Overall structure of the intracellular gate of the outward-facing state viewed from the intracellular side. The residues constituting the gate interactions are shown as stick models. (b,c) Close-up views of the intracellular gate interactions around (b) Asp69 and (c) Asp140. (d) Structural comparison of the intracellular side. The N lobe (left) and the C lobe (right) are separately superimposed, and viewed from the intracellular side. The disordered part of the Glu368 side chain is indicated as grey sticks. (e) Superimposed N lobe (left) and C lobe (right), viewed from the membrane plane. (f) Overall structures of the extracellular gate of the inward-facing state viewed from the extracellular side. The residues constituting the gate interactions are shown as stick models, with CPK models superimposed. (g) Structural comparison of the extracellular side. The N lobe (left) and the C lobe (right) are separately superimposed, and viewed from the extracellular side. In d,e,g the relative motions of the helices in the inward-facing state, as compared with the outward-facing state, are indicated by red arrows. All of the models are coloured in the same manner as in Fig. 2.