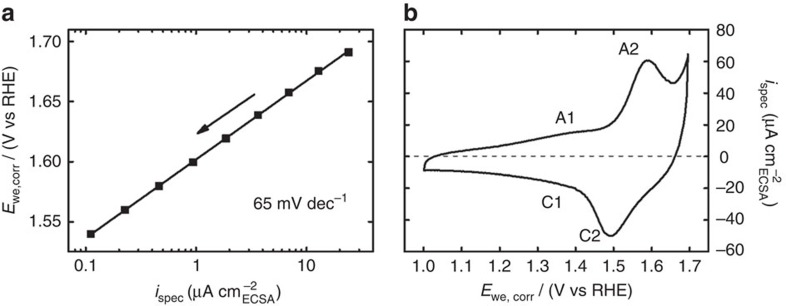
Figure 2. Electrochemical characterization of Co3O4 films.
Tafel plot (a) and cyclic voltammogram (b) of Co3O4 films deposited on glassy carbon recorded in 0.1 M KPi at pH 7. The Tafel plot was extracted from cathodic quasi-stationary potential-step rotating disc electrode experiments after equilibration for 4 min at each potential; the line corresponds to a Tafel slope and an exchange current density of 65 mV dec−1 and 2.26 × 10−9 mA cm−2ECSA, respectively. The cyclic voltammogram was recorded with a scan rate of 100 mV s−1 and shows a minor and major Co redox feature at ∼1.4 V (A1/C1) and ∼1.54 V (A2/C2), respectively. The capacitance-corrected reductive charge of the two redox features showed that only ∼1.8% of the Co ions change their oxidation state by one equivalent. Electrode potentials were corrected for Ohmic losses and are referred to reversible hydrogen electrode (RHE). The current was normalized using electrochemical surface area (ECSA) as determined by potentiostatic electrochemical impedance spectroscopy14. The electrochemical surface roughness was 26.4.