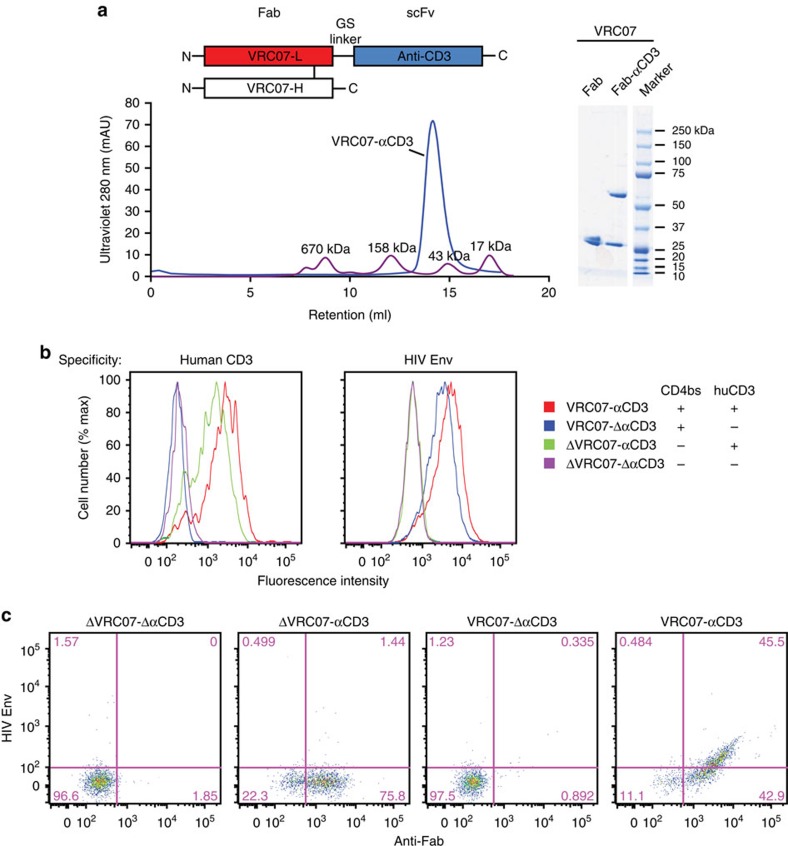
Figure 1. Bispecific immunomodulatory protein binds the CD4-binding site (CD4bs) of HIV Env and CD3.
(a) Molecular characterization of the bispecific immunomodulatory protein. The chromatogram of VRC07-αCD3 run through a size exclusion column shows the correct molecular size for the bispecific antibody (left). The heavy and light chain fragments of indicated Fab and bispecific antibodies were analysed by reducing SDS–PAGE gel (right). (b) VRC07-αCD3 binds to CD3 and HIV-1 Env on the cell surface. Human T cells and HIV-1-infected CEM cells were incubated with bispecific antibodies of the indicated specificities, and bound antibodies were detected by a fluorescein isothiocyanate-conjugated anti-Fab probe. (c) The indicated immunodulatory bispecific and control proteins were allowed to bind to naive human T cells and any protein bound to the T cells was detected with flow cytometry after dual staining with fluorescently labelled anti-human Fab and HIV-1 Env (RSC3) probes.