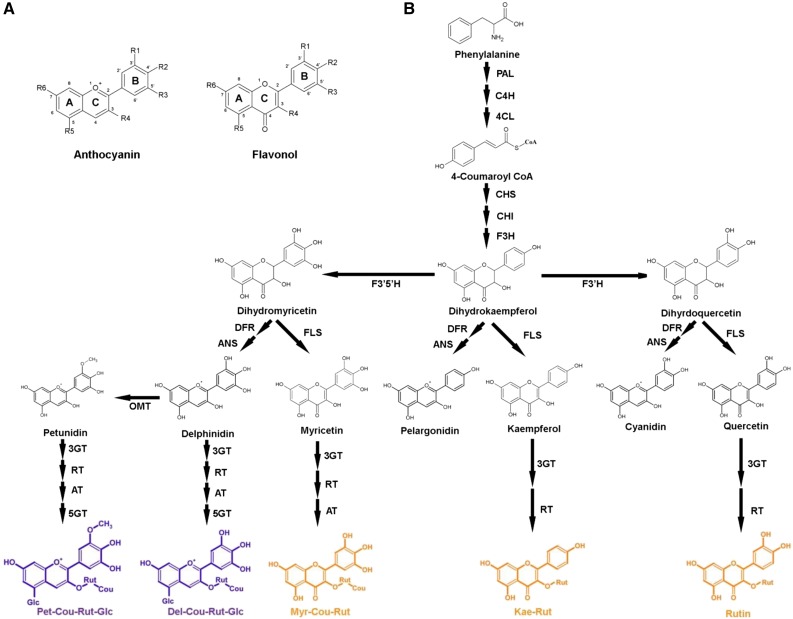
Figure 1.
Flavonoid biosynthesis pathway in tomato. A, Basic structures of an anthocyanin and a flavonol. Common modification positions include 3′ (R1), 4′ (R2), 5′ (R3), 3 (R4), 5 (R5), and 7 (R6) of each ring. B, Schematic representation of the flavonoid biosynthetic pathway in tomato. Compounds highlighted in purple are the major anthocyanins identified in tomato fruit, and major flavonols are highlighted in orange. From the top, abbreviations are as follows: PAL, Phe ammonia lyase; 4CL, 4-coumarate:CoA ligase; C4H, cinnamate 4-hydroxylase; C3H, 4-coumarate 3-hydroxylase; CHS, chalcone synthase; CHI, chalcone isomerase; F3′H, flavonoid-3′-hydroxylase; FLS, flavonol synthase; DFR, dihydroflavonol reductase; ANS, anthocyanidin synthase; 3GT, flavonoid 3-O-glucosyltransferase; RT, flavonoid 3-O-glucoside-rhamnosyltransferase; AT, anthocyanin acyltransferase; 5GT, flavonoid-5-glucosyltransferase; and OMT, O-methyltransferase.