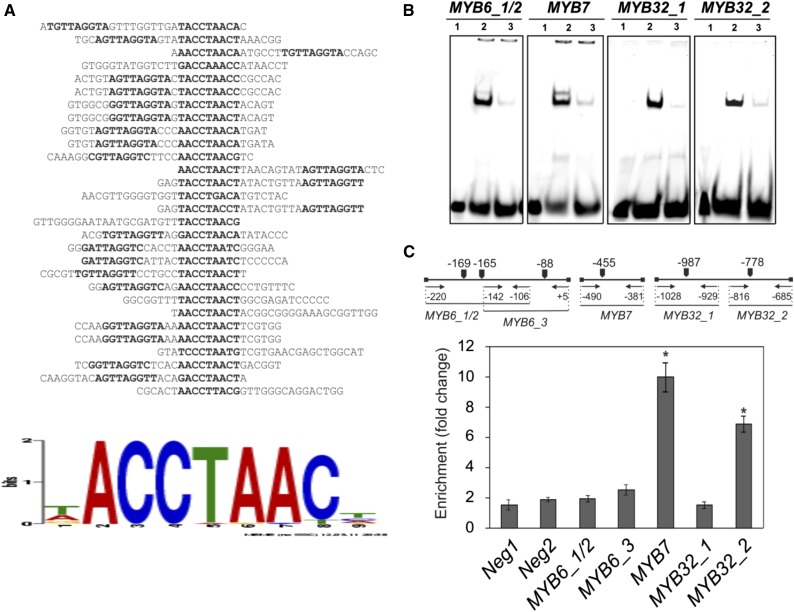
Figure 9.
Identification of MYB112 direct target genes. A, MYB112 in vitro binding site selection. A motif common to 29 positive clones was identified using MEME. The motif is present in the promoters of putative direct target genes. B, EMSA. Purified MYB112-CELD-His protein binds specifically to the MYB112 binding sites present in the MYB6, MYB7, and MYB32 promoters. In vitro DNA binding reactions were performed with 40-bp double-stranded oligonucleotides, including the MYB112 binding sites of the respective target gene promoters. The DNA fragments were labeled with IR dye. The fragments contained two (MYB6_1/2) or one (MYB7, MYB32_1, and MYB32_2) MYB112 binding motif. 1, IR-labeled DNA fragment.; 2, MYB112 protein with labeled DNA fragment (note distinct shift indicating binding); 3, MYB112 protein plus labeled DNA fragment and 200× excess competitor (note the shift disappearance). C, ChIP-qPCR. Whole shoots of 2-week-old Arabidopsis seedlings expressing GFP-tagged MYB112 under the control of 35S CaMV promoter (35S:MYB112-GFP) and wild-type plants were harvested for the ChIP experiment. qPCR primer locations are indicated. Primers annealing to promoter regions of two Arabidopsis genes lacking MYB112 binding sites (i.e. At2g22180 [Neg1] and At3g1840 [Neg2]) were used as negative controls. Enrichment of the respective promoter fragments was quantified by qPCR. Data represent means ± sd of three experiments. Enrichment of MYB7 and MYB32 promoter fragments is detected. *, Statistically significant differences to controls as determined by Student’s t test (P < 0.05).