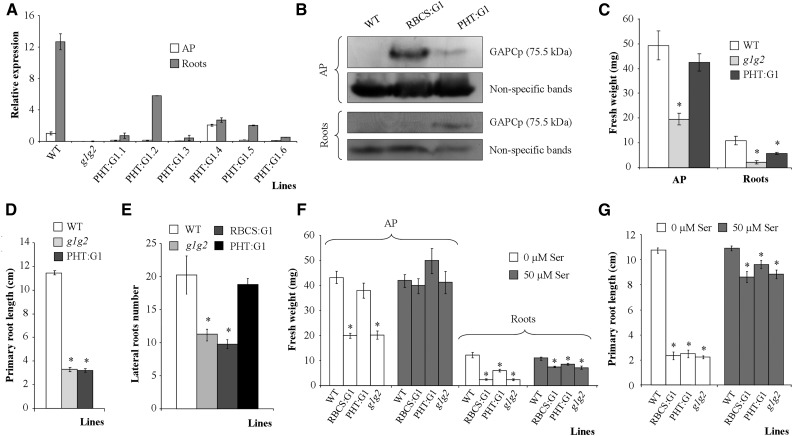
Figure 3.
Molecular and phenotypical analyses of gapcp1gapcp2 (g1g2) expressing GAPCp1-GFP under the control of the PHT promoter (PHT:G1). A, qRT-PCR analysis of GAPCp1 in the APs and roots of several 21-d-old PHT:G1 lines as compared with g1g2 and the wild type (WT). B, Immunoblot showing GAPCp1 expression in the APs and roots of representative RBCS:G1 and PHT:G1 lines as compared with the wild type. Protein gel-blot analysis was performed using anti-GFP antibodies. Nonspecific bands are shown as a sample loading control at bottom. C to E, Fresh weight (C), primary root length (D), and lateral root number (E) of 18-d-old wild-type, g1g2, and PHT:G1 plants. F and G, Fresh weight (F) and primary root growth (G) of wild-type, g1g2, RBCS:G1, and PHT:G1 lines in the absence or presence of 50 µm Ser. In A, values are means ± se of three independent biological replications. In C to E, values are means ± se of two independent transgenic lines (n ≥ 36 plants). In F and G, values are means ± se (n ≥ 40 plants). Asterisks indicate significant differences as compared with the wild type (P < 0.05).