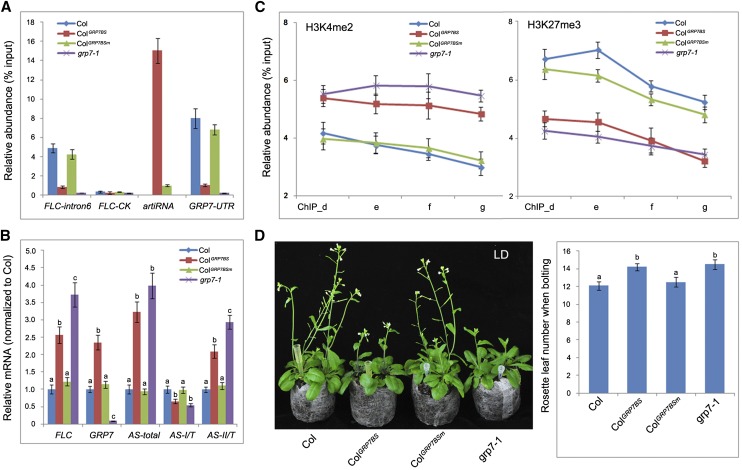
Figure 8.
Reducing GRP7 binding influences COOLAIR process and flowering. A, Competing the binding of GRP7 to its target RNA by artificial RNA fragments reduced the binding of GRP7 to FLC antisense premRNA. RIP was followed by qPCR to check the relative abundance of GRP7 binding at FLC-intron6, FLC-CK, GRP7-UTR, and artificial RNA fragments. Adaptor primers were used in RT. ColGRP7BS, Col with abundant expression of an RNA fragment containing the GRP7-binding site; ColGRP7BSm, Col with abundant expression of an RNA fragment containing a mutated GRP7-binding site. B, Relative expression level of sense FLC, GRP7, and different polyadenylated FLC antisense (AS) mRNAs in Col, artificial RNA transgenic plants, and the grp7-1 mutant. C, Histone modification change (H3K4me2 and H3K27me3) at FLC gene body regions (ChIP_d, e, f, and g as in Fig. 7A) in Col, artificial RNA transgenic plants, and the grp7-1 mutant. D, Flowering time (morphology, left; rosette leaf number when bolting, right) changes in Col, artificial RNA transgenic plants, and the grp7-1 mutant. Tukey’s HSD test was used for B and D, and different letters within the same genetic background indicate statistically significant differences.