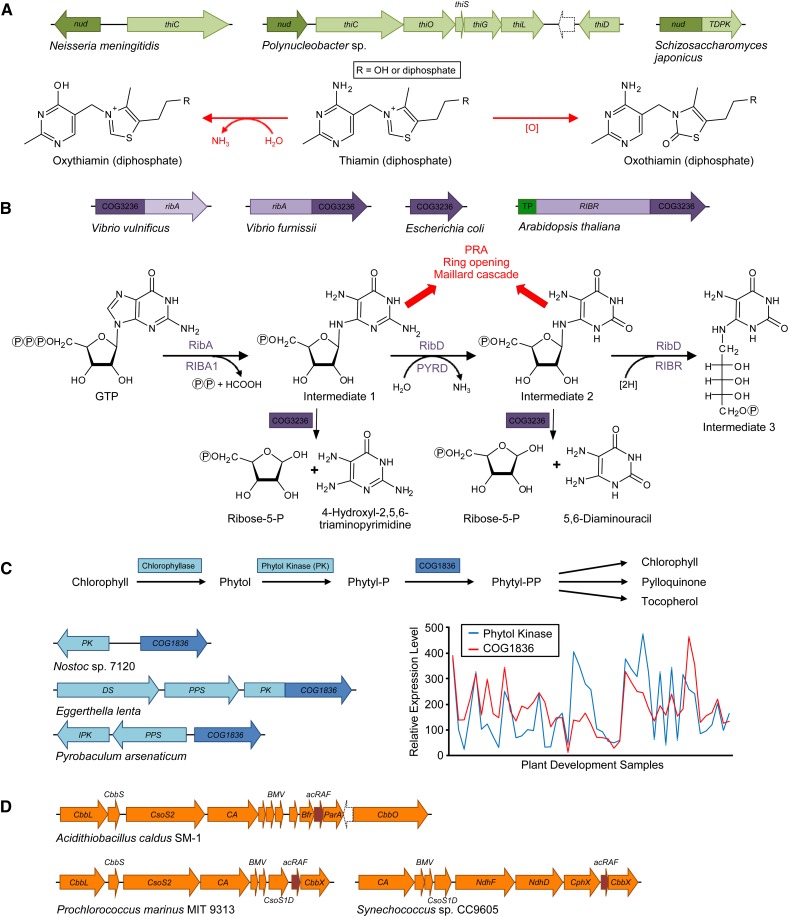
Figure 2.
Clues to the function of unknown plant enzymes and transporters can come from cross-kingdom comparative genomics and plant-based data. A, The nudix (nud) gene encoding the Nudix enzyme (dark green) that preempts damage in thiamin metabolism is fused to, or clusters with, thiamin biosynthetic genes (pale green) in certain bacteria and fungi. The Nudix enzyme preferentially dephosphorylates the thiamin diphosphate analogs oxythiamin and oxothiamin diphosphate and prevents their inhibitory effects on thiamin diphosphate-utilizing enzymes. thi, Thiamin biosynthesis genes. B, The N-glycosidase COG3236 is fused to the riboflavin biosynthesis genes (lilac) ribA in some bacteria or RIBR in plants; COG3236 deglycosylates excess reactive riboflavin intermediates to fairly innocuous ribose-5-phosphate and pyrimidine moieties, preventing ring opening and Maillard reactions, which give rise to very harmful products. PRA, 5-Phosphoribosylamine; TP, targeting peptide. C, The COG1836 gene (dark blue) clusters with genes of polyprenoid metabolism (light blue) in several bacteria, and COG1836 is also fused to phytol kinase in some species. Expression of COG1836 and phytol kinase is correlated during Arabidopsis development (http://csbdb.mpimp-golm.mpg.de/csbdb/dbxp/ath/ath_xpmgq.html). DS, Phytoene desaturase; PPS, polyprenyl pyrophosphate synthetase; IPK, isopentenyl phosphate kinase. D, The pterin-4a-carbinolamine dehydratase (PCD) paralog, α-carboxysome Rubisco assembly factor (acRAF; dark orange), is associated with α-carboxysome gene clusters (orange). CbbL and CbbS, Rubisco large and small subunit; CsoS2, shell protein of unknown function; CA, carbonic anhydrase; BMV, bacterial microcompartment vertex shell proteins; Bfr, bacterioferritin family; ParA, partitioning A family; CbbO, CbbQ activase; CsoS1D, double domain shell protein; CbbX, Rubisco activase; NdhF, complex I NADH oxidoreductase chain F family protein; NdhD, complex I NADH dehydrogenase oxidoreductase M family; CphX, CO2 hydration protein.