Figure 1.
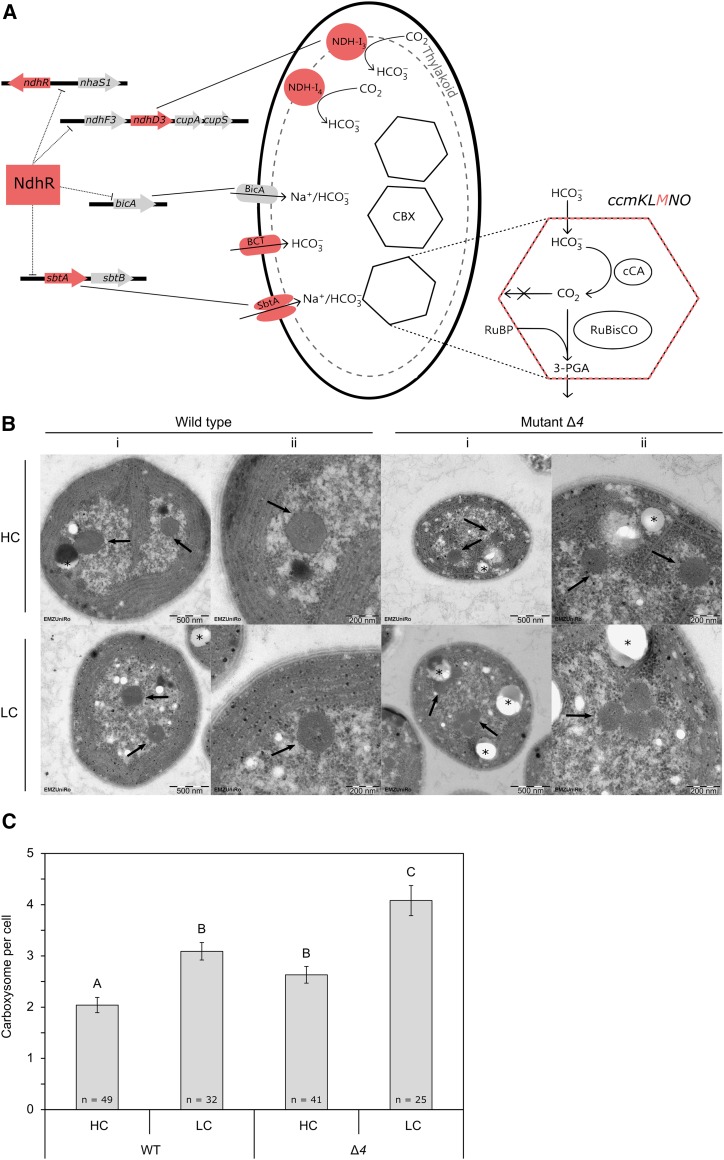
The Synechocystis 6803 mutants of this study and their respective deficiencies. A, The ∆4 mutant is a quadruple carbon transporter mutant that lacks four of the five HCO3−/CO2-uptake systems known in Synechocystis 6803 (Shibata et al., 2002; Xu et al., 2008). The ∆4 mutant is compared with the ∆ndhR mutant (Klähn et al., 2015) and the ΔccmM mutant (Hackenberg et al., 2012). NdhR is a central regulator of carbon metabolism in Synechocystis 6803 and, among others, a repressor of ndhD3 and sbtA. NdhR expression is feedback regulated by autorepression. Note that the expression of the deleted genes ΔndhD4 and ΔcmpA, which are part of the NDH-14 and BCT1 transporter complexes, is not controlled by NdhR. CmpA is part of the cmpABCD operon, which is controlled by the transcriptional regulator CmpR. The ΔccmM mutant does not express CcmM, one of the shell proteins of carboxysomes (CBX) that is encoded in the ccmKLMNO operon and serves as a reference mutant with a carboxysomeless phenotype (Hackenberg et al., 2012). (This scheme was modified from Daley et al. [2012] and Rae et al. [2013]). B, Electron micrographs of Synechocystis 6803 wild type and the ∆4 mutant under HC and LC conditions. Arrows indicate carboxysome cross sections within cells. Polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) bodies are marked by asterisks. i = 23,000-fold original magnification, and ii = 50,500-fold original magnification. C, Number of carboxysomes in Synechocystis 6803 wild type (WT) and the ∆4 mutant under HC and LC conditions. Each bar represents the average number of carboxysomes per cell, and error bars indicate se. Significant differences between sample groups were assessed by heteroscedastic Student’s t test and are indicated by different letters (P < 0.01).