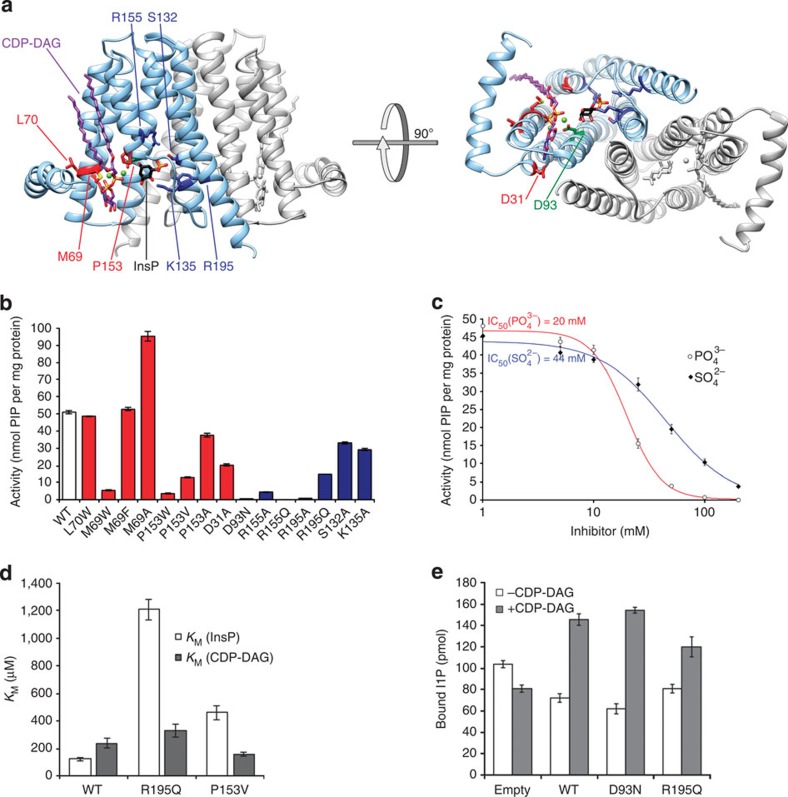
Figure 4. A homology model of MtPIPS, with functional characterization of selected point mutants.
(a) The MtPIPS homology model is shown in ribbon representation with one protomer in grey and the other in light blue, from two views, on the left viewed in the plane of the membrane and on the right from the cytosol, along the dimer axis. The substrates, CDP-DAG (purple) and inositol phosphate (black), are modelled based on the structures of RsPIPS-FL (in complex with CDP-DAG) and RsPIPS-Δ6N (with bound SO42−). The homology model was generated using the Phyre2 server36, in one-to-one threading mode using the sequence of MtPIPS (Uniprot accession: P9WPG7) as the target and the structure of RsPIPS-FL (with the Af2299 extramembrane domain excised) as the template. Selected residues which are predicted to participate in either inositol phosphate binding (R155, R195, S132, K135), CDP-DAG binding (P153, M69, D31), neither (L70), or catalysis (D93) are shown with side chains in stick representation and coloured as in (b), where the activity of point mutants at these positions for the MtPIPS-FL construct is shown compared to wild-type MtPIPS-FL. (c) 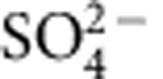 (closed diamonds) and
(closed diamonds) and 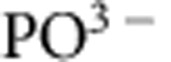 (open circles) inhibit the activity of MtPIPS-FL with half-inhibitory concentrations of 44 and 22 mM, respectively. (d) KM of MtPIPS-FL WT, R195Q and P153V for inositol phosphate (InsP; white) and CDP-DAG (grey). InsP, L-myo-inositol-1-phosphate (inositol phosphate). (e) Quantification of bound L-myo-[14C]inositol-1-phosphate after incubation of liposomes containing 9 μg MtPIPS-FL (WT, D93N, R195Q or empty liposome control) in the presence and absence of 200 μM CDP-DAG with 40 μM L-myo-[14C]inositol-1-phosphate. Measurement errors were quantified as s.e.m. (n=3).
(open circles) inhibit the activity of MtPIPS-FL with half-inhibitory concentrations of 44 and 22 mM, respectively. (d) KM of MtPIPS-FL WT, R195Q and P153V for inositol phosphate (InsP; white) and CDP-DAG (grey). InsP, L-myo-inositol-1-phosphate (inositol phosphate). (e) Quantification of bound L-myo-[14C]inositol-1-phosphate after incubation of liposomes containing 9 μg MtPIPS-FL (WT, D93N, R195Q or empty liposome control) in the presence and absence of 200 μM CDP-DAG with 40 μM L-myo-[14C]inositol-1-phosphate. Measurement errors were quantified as s.e.m. (n=3).