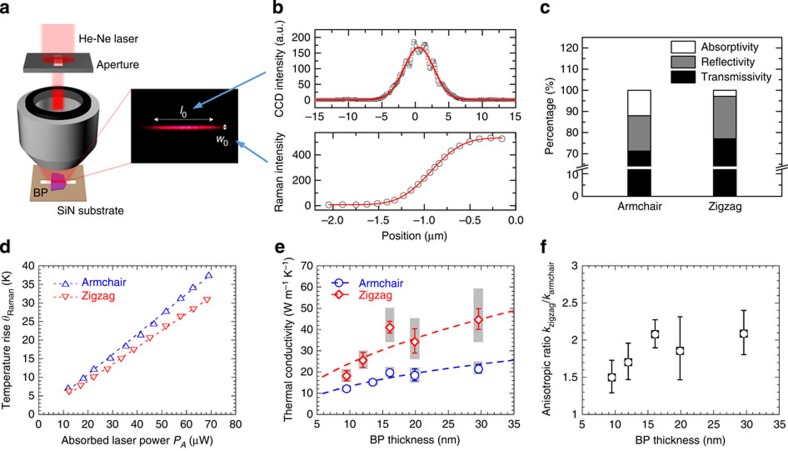
Figure 3. Thermal conductivity measurements of BP using micro-Raman technique.
(a) Illustration of the experimental setup and an optical image of the produced laser focal line. (b) The lengthwise profile and the knife-edge-measured widthwise integrated profile of the laser focal line. The solid lines are Gaussian function and error function curve fits, respectively. (c) The optical absorptivity A, reflectivity R and transmissivity T of the 9.5-nm-thick suspended BP film on armchair- and zigzag-polarized laser incidence. (d) Laser-power-dependent temperature rise (θRaman) of the 16.1-nm-thick BP film determined by the micro-Raman spectroscopy along armchair and zigzag transport directions. The dashed lines are linear fits. (e) Extracted armchair and zigzag in-plane thermal conductivities (karmchair and kzigzag) of multiple BP films. Dashed lines are results of theoretical modelling. The grey error bars account for the uncertainty of SiN substrate thermal conductivity kSiN, whereas the blue/red error bars do not. (f) The anisotropic ratio kzigzag/karmchair at different BP thicknesses. The ratio at 12-nm thickness is calculated using linearly interpolated armchair thermal conductivity from adjacent thicknesses.