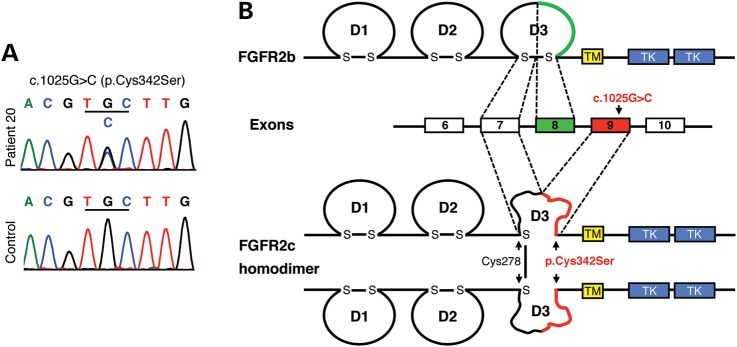
Figure 2.
DNA sequencing identifies a heterozygous c.1025G>C (p.Cys342Ser) missense mutation in the FGFR2c isoform. (A) Electropherograms showing a doublet G/C peak at c.1025 in Patient 20 and a single G peak in the control. (B) Location and biochemical consequences of the FGFR2c-Cys342Ser substitution: FGFR2 contains an extracellular ligand-binding region composed of three immunoglobulin-like domains (D1–D3), a transmembrane domain (TM) and a split cytoplasmic TK domain. FGFR2 exists in two isoforms, FGFR2b and FGFR2c, which are generated by alternative splicing of the C-terminal half of the D3. The c.1025G>C mutation leads to a cysteine-to-serine substitution at position 342 (p.Cys342Ser) in the FGFR2c isoform. Cys342Ser results in loss of the D3 intrachain disulfide bond in FGFR2c and thus to major disruption of the D3. However, the unpaired Cys278 residues form intermolecular disulfide bonds between the mutant receptors resulting in constitutively activated stable FGFR2c homodimers.