Fig. 6.
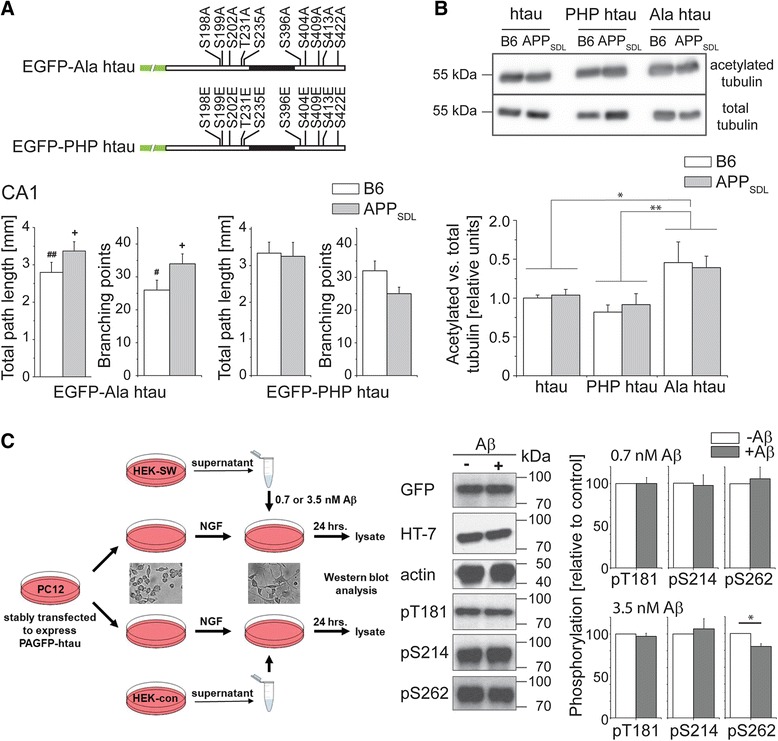
Effect of phosphoblocking and phosphomimicking tau on dendritic simplification. a Total path length and number of branching points of CA1 neurons that express phosphoblocking (Ala htau) or phosphomimicking tau (PHP htau). Schematic representations of the respective construct are shown on the top. Mutated residues are indicated. Ala htau causes dendritic simplification on a non-transgenic background, whereas PHP htau behaves neutral. b Ratio of acetylated to total tubulin as a marker for microtubule stabilization. Immunoblots showing staining against acetylated tubulin and total tubulin (top) and the respective quantitation (bottom). Expression of Ala htau causes stabilization of microtubules. c Effect of low nanomolar concentrations of naturally secreted Aβ on the phosphorylation of tau in model neurons. A schematic representation of the experimental approach is shown to the left. Neuronally differentiated PC12 cells expressing PAGFP-tagged human tau are incubated with a supernatant from Aβ-expressing cells (HEK-SW) or the respective controls (HEK-con). Representative Western blots and quantification of phosphorylation at selected sites is shown to the right. 3.5 nM Aβ induce dephosphorylation of tau at S262. (+) indicate significant increase, (#, ##) significant reduction compared to neurons expressing wildtype human tau. Statistical evaluation was performed using one way ANOVA with post hoc Fisher’s LSD test for multiple comparisons (a) and Student’s t test for comparison of the constructs (b) and the two genotypes (c). Values are shown as mean and s.e.m. See Table 1 for details on the statistics. For (c), 3–10 Western blot experiments were evaluated per condition. *(#)(+), p < 0.05, **(##), p < 0.01
