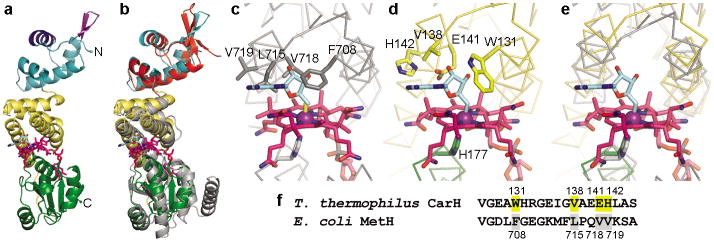
Figure 2.
Structure of CarH protomer and comparison to MetH. (a) CarH protomer colored by domain: N-terminal DNA-binding domain (cyan) with recognition helix (dark blue) and β-hairpin wing (purple) highlighted; central four-helix bundle (yellow); C-terminal Cbl-binding domain (green). AdoCbl shown with Cbl carbons in pink, 5′-dAdo group carbons in cyan, cobalt in purple. (b) Overlay of CarH protomer with Cbl-binding module of MetH (gray, PDB ID code 1BMT17) and BmrR DNA-binding domain (red, PDB ID code 1EXJ38). (c) MetH binds MeCbl (methyl group in yellow); modeling 5′-dAdo (cyan) results in steric clashes. (d) CarH accommodates AdoCbl through several substitutions compared to MetH. Cobalt-coordinating His in green. (e) Superposition of MetH and CarH, highlighting shift of the four-helix bundle between MetH (gray) and CarH (yellow). (f) Alignment of CarH and MetH sequences involved in binding the Cbl upper face, highlighting substitutions.