Figure 3.
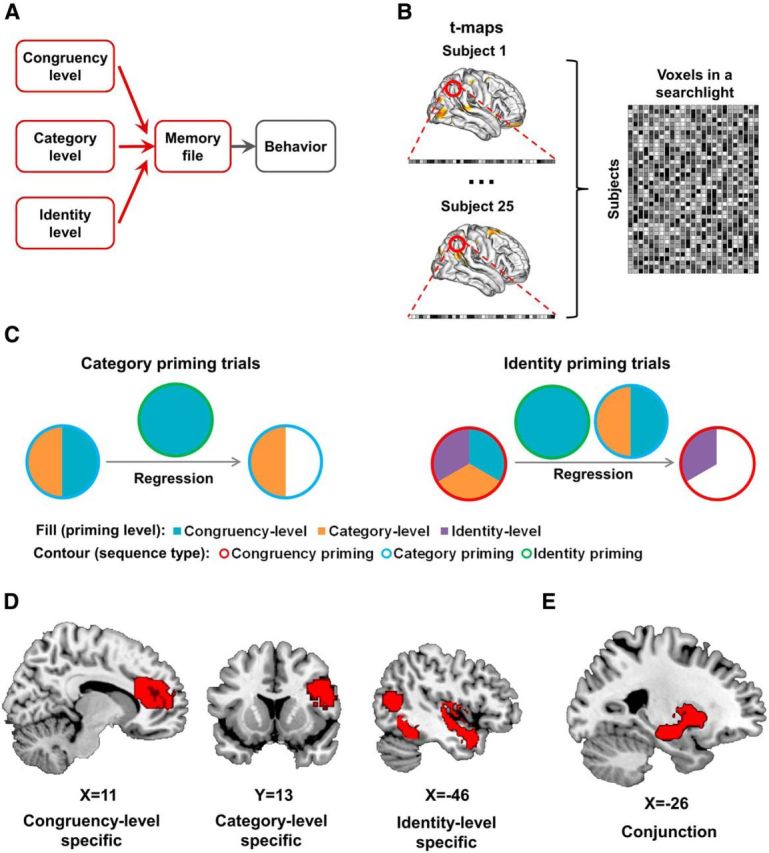
Event-feature-priming MVPA results. A, Within the context of the event file model (Fig. 1A), the present analysis examines the integration of different event features in memory (highlighted in red). B, Illustration of the cross-subject classification MVPA. Given a searchlight, activation of voxels in this searchlight was extracted from individual t-maps and grouped together for cross-subject analysis. C, Schematic illustration of isolating neural congruency effects for each level of priming. Neural congruency effects from the congruency priming condition were regressed from category priming trials and congruency-level and category-level neural congruency effects were regressed from those of identity-priming trials. D, Brain regions displaying feature-level-specific expression of priming effects [i.e., showing higher decoding accuracy for one feature level than the other two levels (p < 0.05, corrected)]; for full results, see Table 1. E, Overlap of searchlights in left putamen and hippocampus (in red) showing above-chance encoding of feature priming at all three levels of abstraction.
