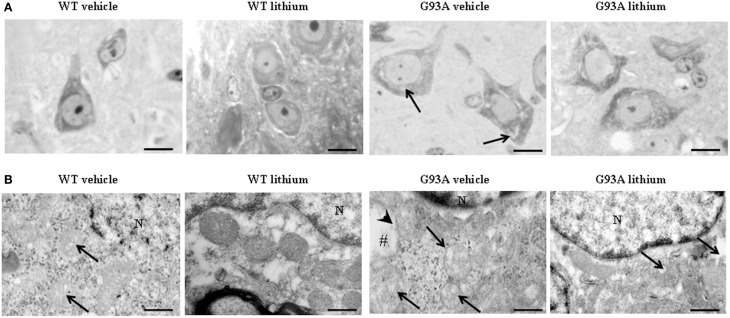
Figure 2.
Representative pictures at light microscopy and transmission electron microscopy of motor neurons. (A) Semi-thin sections are obtained from lamina IX region of the anterior horn of mice spinal cord stained with methylene and toluidine blue. In WT and G93A mice motor neurons appear as multi-polar cells, where the nucleus is not condensed and the nucleolus is well-evident. Motor neurons were chosen also according to a size exclusion criterion as reported in the Materials and Methods. The size of motor neurons increases in G93A mice administered vehicle. In this group the cytoplasm is filled with large vacuoles (arrows). Following lithium administration, large vacuoles disappear. (B) Motor neurons in the anterior horn were analyzed for TEM ultrastructural morphometry of mitochondria. Mitochondria from WT mice treated with vehicle are regularly shaped with homogeneous matrix. In this group only a few mitochondria possess slightly ballooned cristae (arrows). This architecture is further improved by lithium administration, which increases electron-density of the matrix and the integrity of the cristae. In G93A mice administered vehicle, mitochondria exhibit a partial (arrows) or total (#) matrix dilution and dramatic fragmentation of the cristae (arrowhead). Remarkably, in G93A mice lithium reverses mitochondrial alterations leaving only a few altered mitochondria (arrows). N, nucleus. Scale bars = (A) = 30 μm; (WT vehicle) = 0.46 μm; (WT lithium) = 0.30 μm; (G93A vehicle) = 0.60 μm; (G93A lithium) = 0.5 μm.