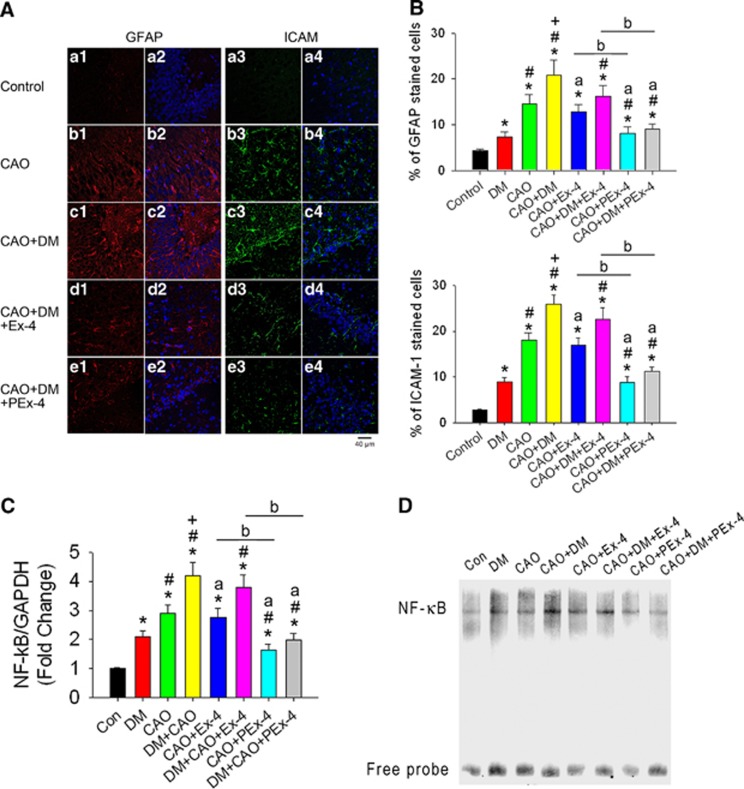
Figure 5.
Effect of exendin-4 (Ex-4) and Ex-4-loaded poly(D,L-lactide-co-glycolide) microspheres (PEx-4) on carotid artery occlusion (CAO)-induced neuroinflammation in control and diabetes mellitus (DM) rats. (A) Positive glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) cells (red fluorescence) and positive intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) cells (green fluorescence) under × 40 magnification were observed in the CA1 area of the hippocampus in the DM, CAO, DM+CAO, DM+CAO+Ex-4, and DM+CAO+PEx-4 groups (n=6 each). (B) GFAP and ICAM-1 immunoreactivity was significantly (P<0.05) increased in DM rats in comparison with control rats (n=6 each). CAO significantly (P<0.05) enhanced GFAP and ICAM-1 expression in control and DM rats. PEx-4 reduced GFAP (P=0.042 vs. CAO+Ex-4; P=0.023 vs. DM+CAO+Ex-4) and ICAM-1 (P=0.021 vs. CAO+Ex-4; P=0.017 vs. DM+CAO+Ex-4) expression more effectively than Ex-4. (C) Cerebral cortical nuclear factor (NF)-κB mRNA/GAPDH (glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase) ratios in eight groups (n=3 each) are shown. There were 2.1-, 2.9-, and 4.2-fold increases in NF-κB/GAPDH ratios, respectively, in the DM, CAO, DM+CAO rats in comparison with the control rats. Compared with DM+CAO rats, these increases in NF-κB (P=0.030) mRNA expression were significantly attenuated in DM+CAO+PEx-4 rats, whereas these increases were not significantly attenuated in DM+CAO+Ex-4 rats. (D) Gel shift of nuclear transcription factor NF-κB by electrophoretic mobility shift assay confirmed the similar findings to NF-κB mRNA/GAPDH ratios. Data are presented as mean±s.e.m.; n=6. Group differences were compared by one-way analysis of variance, followed by Tukey's multiple comparison tests. P<0.05 indicates a significant difference. *Different from control (Con); #different from DM; +different from CAO; adifferent from DM+CAO; bdifferent from the Ex-4-treated group.