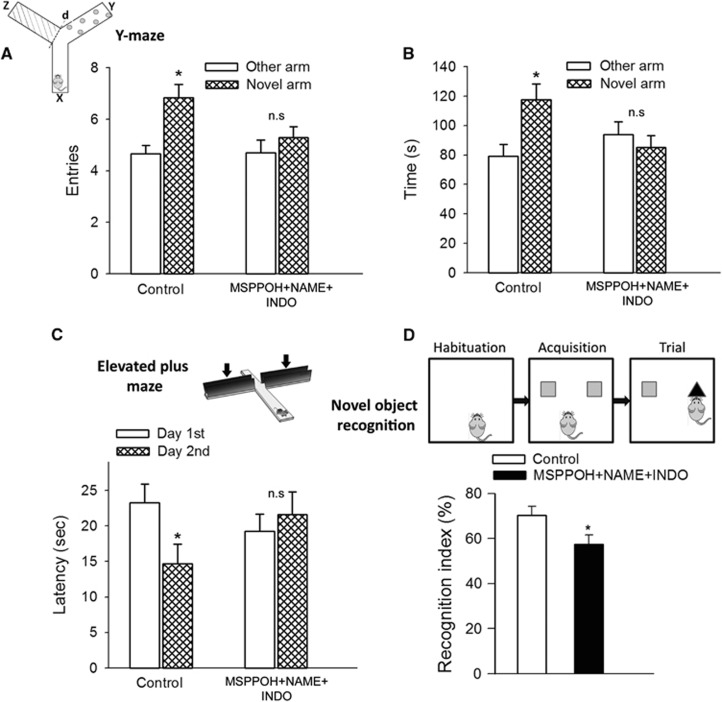
Figure 2.
Neurovascular uncoupling impairs learning and memory. (A and B) Spatial memory testing of mice in Y-maze. The inset shows schematic picture of the Y-maze with extra-maze cues used for testing spatial memory (x: start arm, y: other arm, z: novel arm, see details in text). Number of entries in novel arm (A, *P=0.006 versus other arm in control mice) and exploratory time spent in novel arm of the Y-maze during retrieval trial (B, and P=0.001 versus other arm in control mice) are shown. Mice treated with MSPPOH+NAME+INDO exhibited impaired spatial memory as shown by the similar number of entries (P=0.46) and exploratory time (P=0.36) spent in novel arm and the other arm of Y-maze during the retrieval trial. Data are mean±s.e.m. (n=20 in each group). (C) Neurovascular uncoupling impairs learning ability, as assessed using the elevated plus maze-based learning protocol (see Materials and methods for details). Control mice exhibited significantly decreased transfer latency on day 2 (*P=0.027 versus Day 1) indicating intact hippocampal-dependent learning. For mice treated with MSPPOH+NAME+INDO transfer latency was similar on days 1 and 2 (P=0.71) indicating that these mice had significantly impaired learning ability. Data are mean±s.e.m. (n=20 in each group). (D) The novel object recognition task test is used to evaluate recognition memory in mice (inset). During the habituation phase, the animals explored the empty open-field arena for 5 minutes. Then, in the acquisition phase the mice explored two identical objects during 2 minutes. After a 4-hour delay, a trial phase occurred. The recognition index (representing the time spent investigating the novel object relative to the total object investigation) was used as the main index of retention. Data are mean±s.e.m. (n=20 in each group). *P<0.05 versus control. INDO, indomethacin; MSPPOH, N-(methylsulfonyl)-2-(2-propynyloxy)-benzenehexanamide; l-NAME, l-NG-Nitroarginine methyl ester.