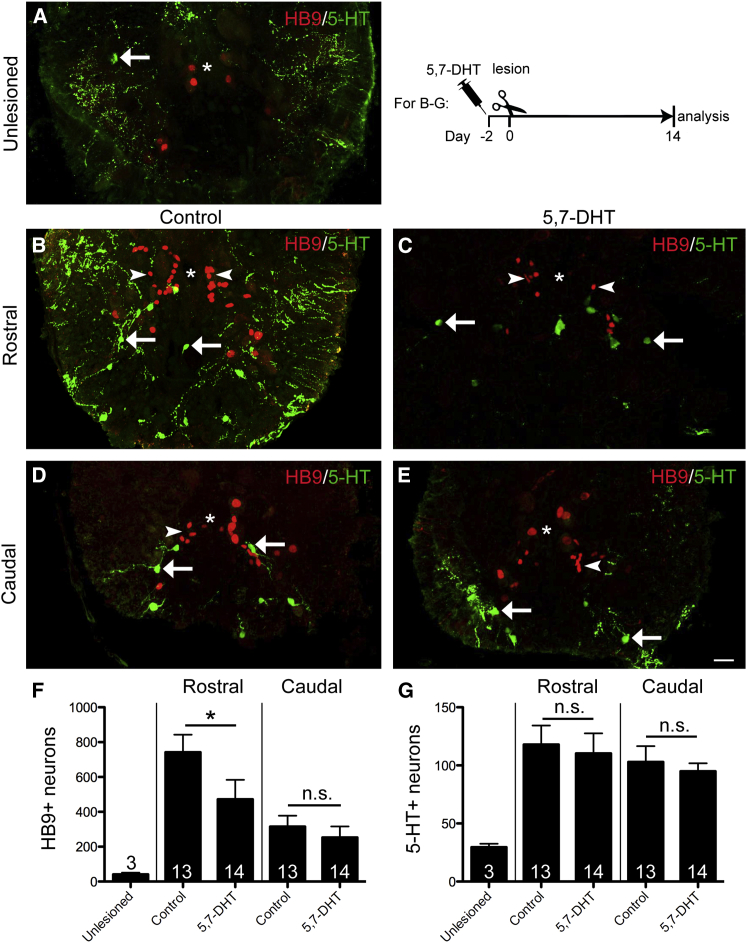
Figure 4.
Ablation of Serotonergic Axons Inhibits Regeneration of Motor Neurons, but Not Serotonergic Neurons
Spinal cross-sections are shown (dorsal is up; asterisk indicates central canal).
(A) In the unlesioned spinal cord, few small HB9+ and motor neurons and 5-HT+ cells (arrow) are present.
(B–G) Rostral to the lesion (see timeline for experimental condition), ablation of serotonergic axons leads to reduced motor neuron (arrowheads) regeneration without influencing regeneration of serotonergic neurons (arrows). Caudal to the lesion, numbers of newly generated motor neurons and serotonergic neurons are unaltered (Mann-Whitney U-test; ∗p = 0.0344). The scale bar in (E) represents 25 μm.
See also Figure S4.