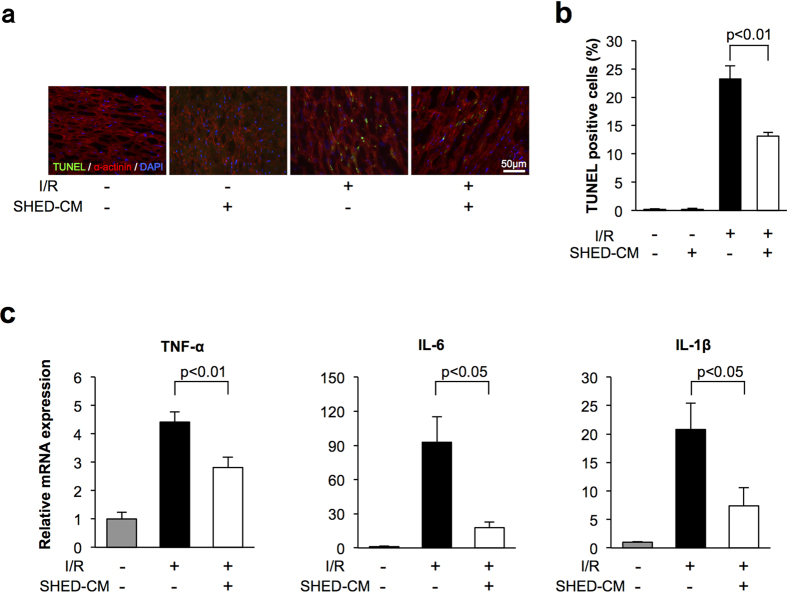
Figure 2. SHED-CM suppressed apoptosis and inflammation in mice following myocardial ischemia-reperfusion.
(a) Representative photographs of heart sections stained with TUNEL from WT mice treated with control and SHED-CM at 24 h after sham operation or myocardial ischemia-reperfusion. Apoptotic nuclei were determined by TUNEL staining (green), and cardiac myocytes were stained with sarcomeric α-actinin (red). Total nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). (b) Quantitative analysis of apoptotic nuclei from WT mice treated with control (n = 5) and SHED-CM (n = 5) at 24 h after sham operation or myocardial ischemia-reperfusion. TUNEL-positive cells were counted in three randomly chosen microscopic fields from five different sections in each tissue block and expressed as a percentage of the total number of nuclei. (c) mRNA levels of TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β in the myocardium in WT mice treated with control and SHED-CM at 24 h after myocardial ischemia-reperfusion. mRNA levels were measured by real-time PCR (n = 5 in each group). All results are normalized to GAPDH. Results are presented as mean ± SEM.