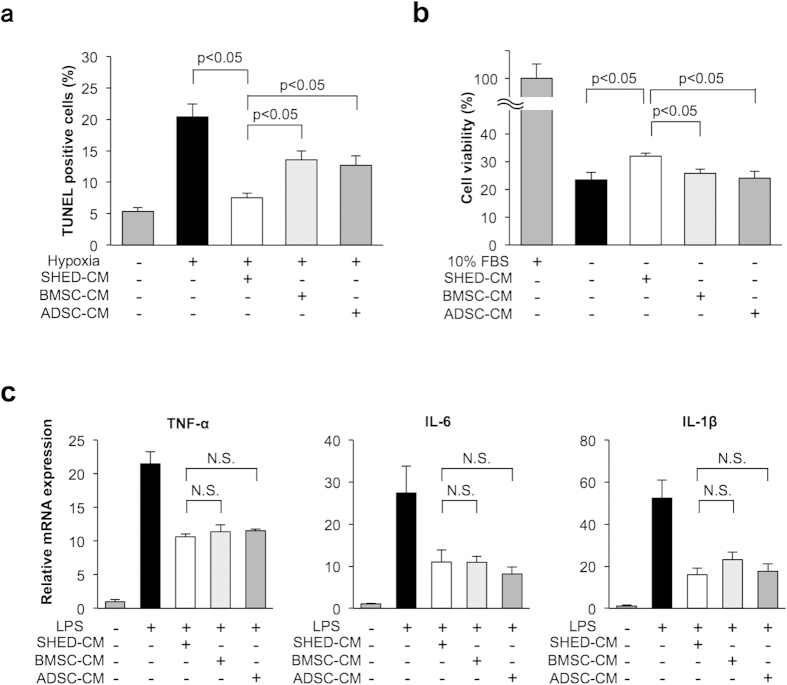
Figure 4. SHED-CM attenuates apoptosis more effectively than BMSC-CM or ADSC-CM in cardiac myocytes.
Cardiac myocytes were treated with SHED-CM, BMSC-CM, or ADSC-CM under 24 h of hypoxia or 48 h of normoxia. (a) Quantitative analysis of TUNEL-positive cardiac myocytes treated with SHED-CM, BMSC-CM, or ADSC-CM under 24 h of hypoxia. TUNEL-positive nuclei were counted in three randomly selected microscopic fields of the three different slides and expressed as a percentage of the total number of nuclei (n = 3 in each group). (b) Cell viability of cardiac myocytes was analyzed by WST-8 assay after 48-h serum deprivation treated with SHED-CM, BMSC-CM, or ADSC-CM. Results are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 3 in each group). Control cells were cultured in DMEM containing 10% FBS. The numbers of surviving cardiac myocytes were expressed as percentage of control cells. (c) Effect of SHED-CM, BMSC-CM, or ADSC-CM on LPS-induced expression of TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β in cardiac myocytes. Cardiac myocytes were pretreated with SHED-CM, BMSC-CM, or ADSC-CM for 1 h and stimulated with LPS (100 ng/ml) for 6 h. The mRNA expression of cytokines was measured by real-time PCR and expressed relative to GAPDH levels (n = 3 in each group). Results are presented as mean ± SEM.