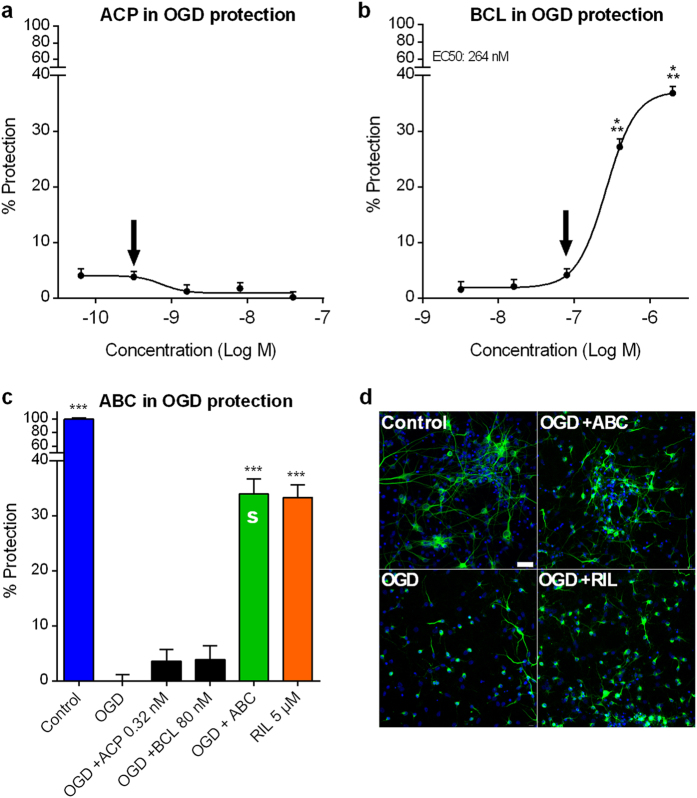
Figure 1. Combination of ACP and BCL acts synergistically to protect cortical neurons from oxidative stress in vitro.
Data are derived from a combined analysis of 2 different experiments with 18 replicates per experiment. Data were normalised to the non-treated control (100%) and oxygen glucose deprived (OGD) cells (0%). Dose-response effect of ACP (a) or BCL (b) following OGD. BCL protected neuronal cells against OGD in a dose-related fashion. At inactive concentrations of individual drugs (Arrows in (a) and (b)), ABC was active with a synergistic effect (S) on cortical neurons (c), assessed by the Highest Single Agent approach (HSA CI = 0.12, P < 2e-16), as visualised in (d) through immunodetection of MAP-2 (green). Experimental validation of the model was performed with Riluzole (RIL). All values are mean ± s.e.m. ***P < 0.001 versus OGD; ANOVA with Dunnett’s test. ABC: ACP 0.32 nM + BCL 80 nM. S: Synergy. Arrows (a,b) indicate the concentrations used in (c). Scale bar: 30 μm. Blue: Hoechst.