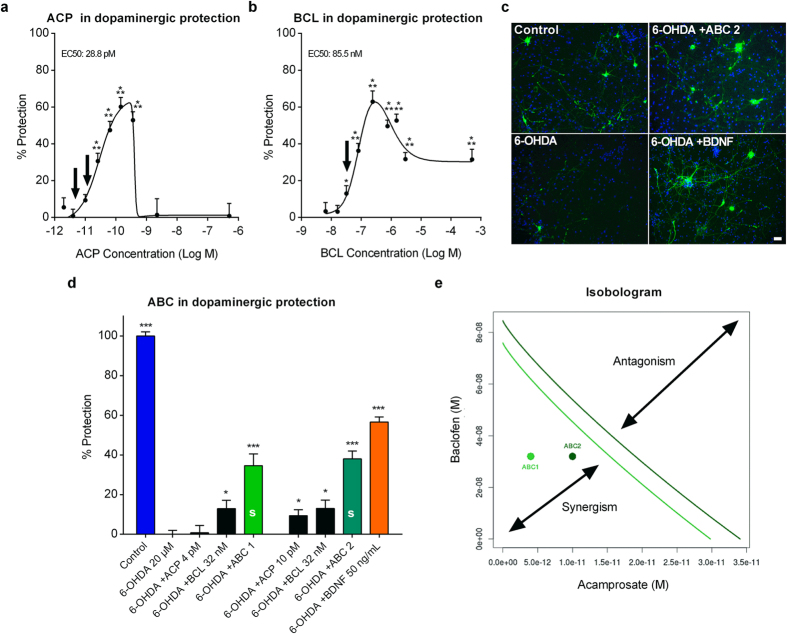
Figure 2. Combination of ACP and BCL acts synergistically to protect dopaminergic neurons intoxicated by 6-OHDA in vitro.
Data are derived from a combined analysis of 5 different experiments with 18 replicates per experiment. Data were normalised to the non-treated control (100%) and 6-OHDA-intoxicated cells (0%). Dose-response of ACP (a) and BCL (b) in 6-OHDA-intoxicated mesencephalic cultures. ACP and BCL effects were dose-dependent and bell-shaped. As visualised in (c) through immunodetection of TH (green), ABC significantly protected dopaminergic neurons more efficiently than its individual drugs when these were used at their inactive or sub-active concentrations (Arrows in (a) and (b)), indicating their positive interaction on dopaminergic neurons (d). BDNF was used as a positive control. (e) Synergy between ACP and BCL of the combined drugs from (a) and (b), assessed by Loewe additivity model and isobologram analysis (Loewe CI = 0.60 for ABC 1 and 0.74 for ABC 2). ABC 1 (green) and ABC 2 (dark green) are each located on the left side of its respective isobole (same colour code), thus meaning that these combinations are synergistic (CI < 1). All values are mean ± s.e.m. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001 versus 6-OHDA; ANOVA with Dunnett’s test. ABC 1: ACP 4 pM + BCL 32 nM. ABC 2: ACP 10 pM + BCL 32 nM. S: Synergy. Arrows (a,b) indicate the concentrations used in (c). Scale bar: 20 μM. Blue: Hoechst.