Figure 5.
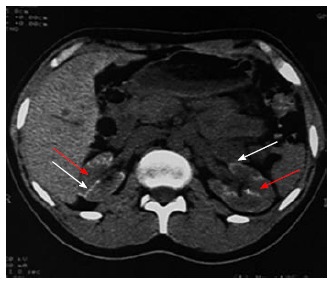
Non contrast computed tomography showing bilateral cortical calcification in a patient with renal cortical necrosis 72 d after acute pancreatitis. Non contrast computed tomography scan of abdomen at the level of renal hila showing linear hyperattenuation along the renal cortical rim (white arrow) with hypoattenuating medulla (red arrow) in bilateral kidney.
