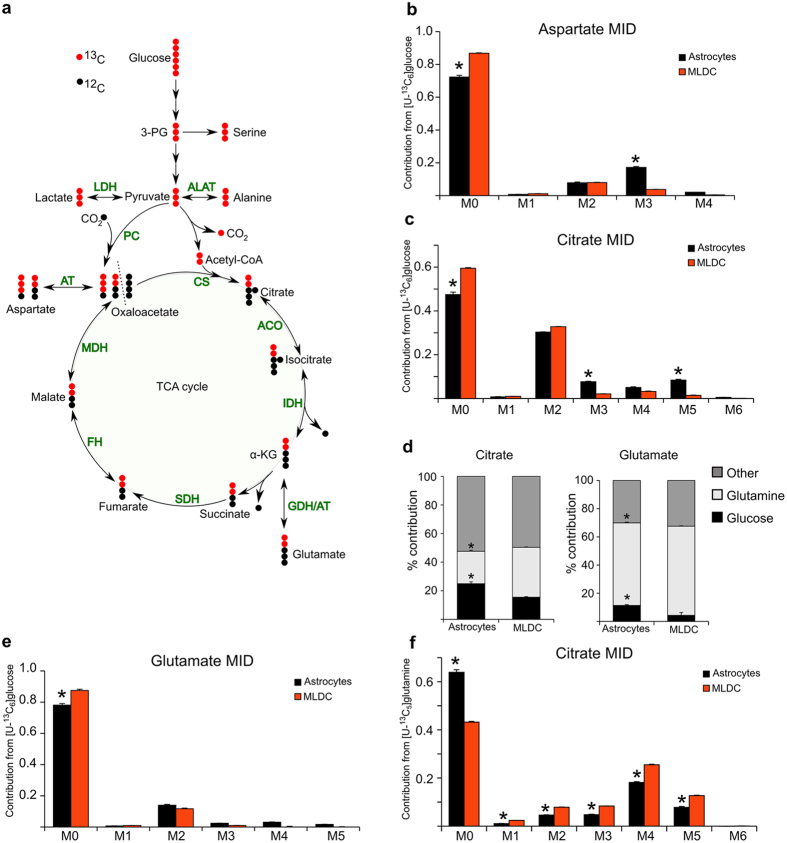
Figure 5. Stable isotope assisted metabolic profiling of hNSCs derived astrocyte.
(a) Atom transition model of uniformly labeled [U-13C]glucose. Glucose derived [U-13C]pyruvate can enter the TCA cycle via pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) dependent oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl-coA. In this case citrate molecules show a mass increase by two (M2 isotopologue). Subsequent TCA cycle metabolites are also M2 isotopologues. As an alternative way to enter the TCA cycle pyruvate can be carboxylated by pyruvate carboxylase, resulting in oxaloacetate M3 isotopologues. The dotted line indicates the start and the end of the cycle. ALAT: alanine aminotransferase; LDH: lactate dehydrogenase; PC: pyruvate carboxylase; CS: citrate synthase; ACO: Aconitase; IDH: isocitrate dehydrogenase; GDH: glutamate dehydrogenase; AT: aminotransferase; SDH: succinate dehydrogenase; FH: fumarate hydratase; MDH: malate dehydrogenase. (b–f) Mass isotopomer distributions (MIDs) and carbon contributions. Cells were labeled for 24h prior extraction of intracellular metabolites and analysis by GC/MS. M1-M6 indicates the number of 13C atoms incorporated into the metabolite. (b) MID of aspartate using [U-13C]glucose as a tracer. (c) MID of citrate using [U-13C]glucose as a tracer. (d) Calculated carbon contribution from gluocose, glutamine and other carbon sources (e.g. lipids, branched chain amino acids) to citrate (left) and glutamate (right). (e) MID of glutamate using [U-13C]gl = 3 independent experiments in triplicate; p-value < 0.05.