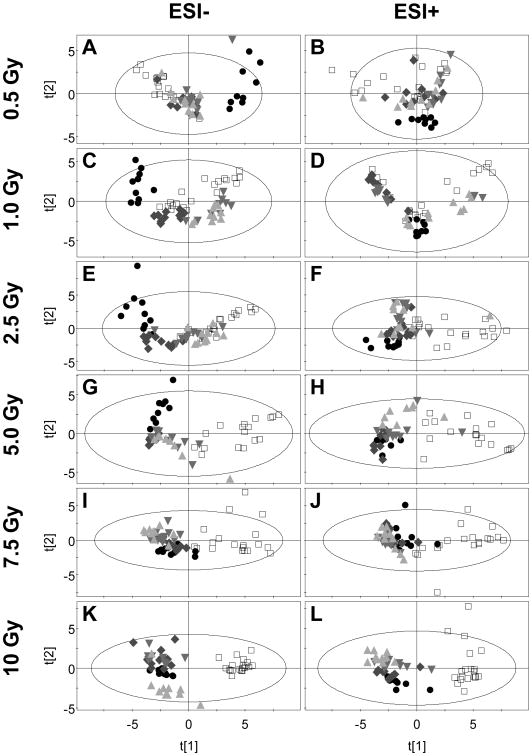
Figure 2.
Principal components analysis shows dose- and time-dependent changes in urine metabolome after exposure to total body irradiation. Urine samples collected from rats before and after exposure to doses of total body gamma radiation ranging from 0.5 to 10 Gy were analyzed by UPLC-TOFMS. Shown are the principal component 2 (t[2]) versus principal component 1 (t[1]) scores for data acquired in both ESI- and ESI+ modes. Six-h (●) urine samples collected after exposure separated in the t[1] axis from pre exposure urine samples (□) at as little as 0.5 Gy (panels A and B). At dose of 1 Gy and above, the first 24-hour (◆) samples separate in the t[1] axis and at doses of 2.5 Gy and higher, the 48-h (▼) and 72-h (▲) urine samples separate in the t[1] axis from pre exposure as well. Ellipses are the boundaries of Hotelling's T2 95% confidence interval.