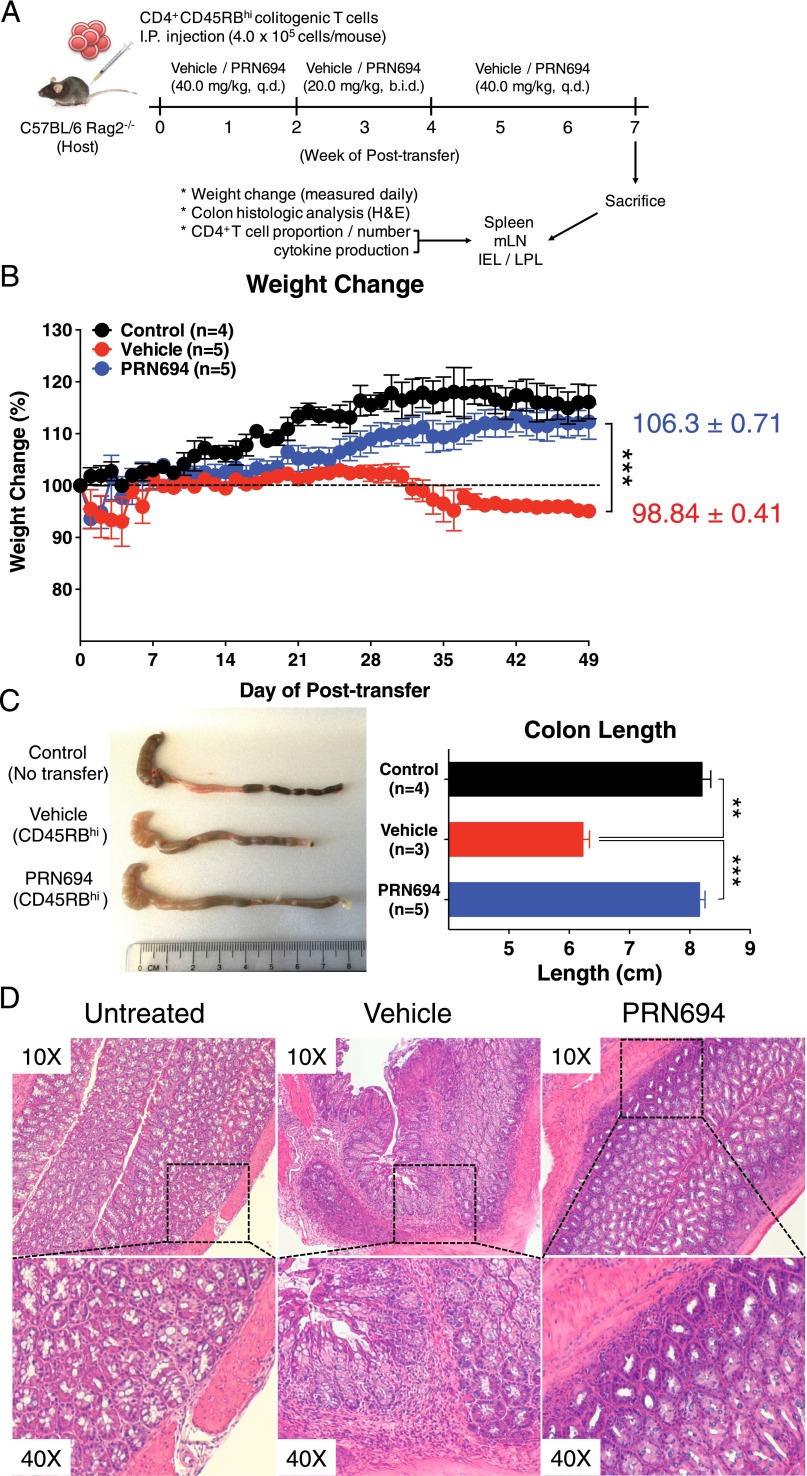
FIGURE 3.
PRN694 administration ameliorates colitis disease progression. (A–D) Colitogenic CD4+CD45RBhi splenic T cells (4.0 × 105 cells/mouse) from C57BL/6 WT mice were injected i.p. into C57BL/6 Rag2−/− hosts. Recipients were treated with vehicle (red, n = 5) or PRN694 (blue, n = 5) with the indicated regimen (A), and disease progression of dosed recipients and untreated (no CD4+CD45RBhi T cell transfer) Rag2−/− controls (black, n = 4) was monitored by weight change (B). Data are shown as means ± SEM. At 7 wk posttransfer, untreated Rag2−/− control, vehicle-dosed, and PRN694-dosed mice were sacrificed for the measurement of colon length (C) and histologic analysis using H&E staining (D). Data were compiled from two independent experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.