Fig. 2.
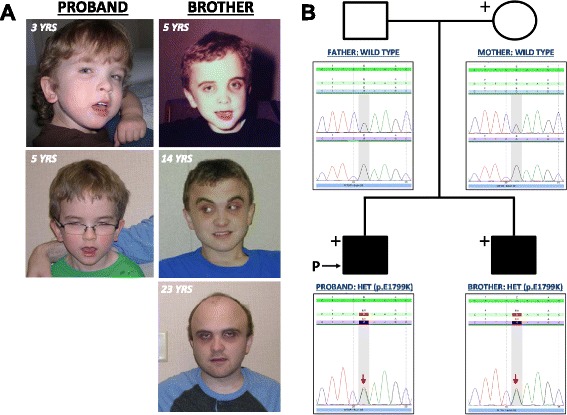
Clinical presentation and co-segregation analysis. a) Photographs of the proband (left column) and his affected brother (right column) at different ages. b) Familial co-segregation/ Sanger sequencing analyses indicate that the affected brothers are heterozygous for MTOR c.5395G>A, p.E1799K (red arrows); in contrast, both parents are homozygous for the wild type allele. These results strongly suggest that c.5395G>A (p.E1799K) arose due to gonadal mosaicism in one of the parents. Chromatograms are shown beneath each member of the pedigree. Note that ‘+’ indicates whole exome sequencing was performed, while open shapes represent unaffected family members; the black shapes represent the affected brothers
