Fig. 2.
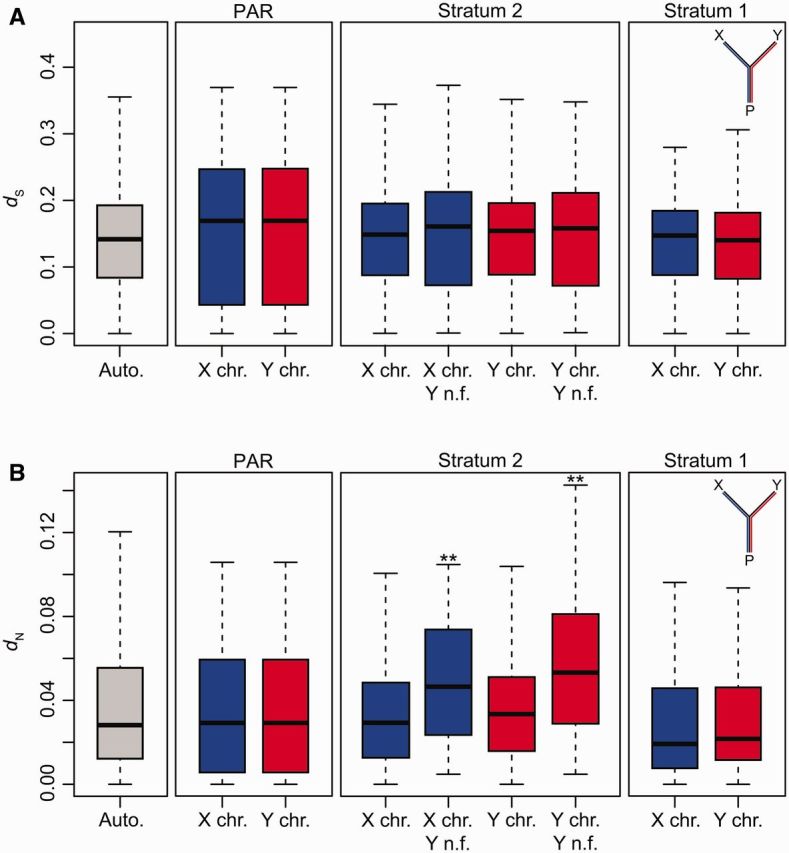
Lineage-specific divergence of the X and Y chromosomes. The X chromosome, Y chromosome, and autosomes of Gasterosteus aculeatus were aligned to the ninespine stickleback (Pungitius pungitius) to quantify (A) synonymous site divergence (dS) and (B) nonsynonymous site divergence (dN) between G. aculeatus and P. pungitius orthologs (autosomes: N = 27,858 genes; PAR: N = 87 genes; stratum 2: N = 490 genes; stratum 2 non-functional (n.f.): N = 92 genes; stratum 1: N = 75 genes). n.f. genes are those that include frameshifts or nonsense mutations on the Y chromosome. Significant differences among groups were determined using a Kruskal–Wallis test. Groups significantly different from the autosomes using a post hoc Mann–Whitney U test (corrected for multiple comparisons) are indicated with asterisks (**P < 0.05). Whiskers are 1.5 × the interquartile range. Outliers are not shown.
