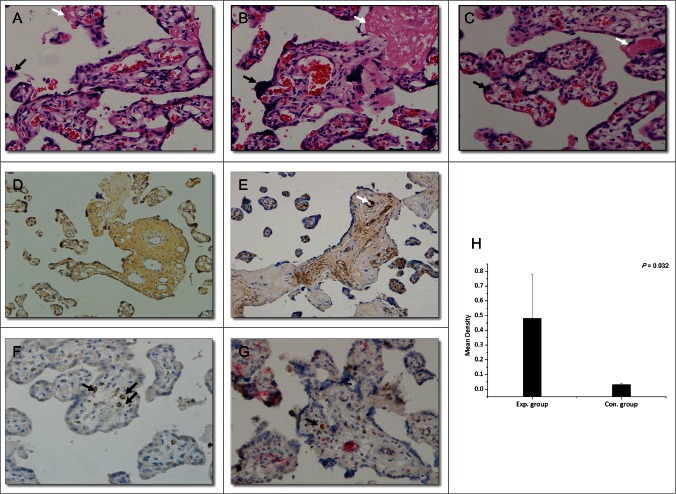
Figure 3.
Histopathological changes in the placenta (hematoxylin-eosin; magnification, ×200, A–C) and immunohistochemical staining (magnification, ×200, D–F: DAB staining, G: DAB and AP-Red staining). (A) Section of placenta from late pregnancy of a healthy woman. (B) Section of placenta from a woman in the control group (HBV-infected women without HBIG injections). (C) Section of placenta from a woman in the experimental group (HBV-infected women receiving HBIG injections). Black arrows: syncytial knotting; white arrows: fibrinoid necrosis. (D) HBsAg staining. (E) HBIG staining. White arrow: villous capillary endothelial cells. (F) CD68 staining. Black arrows: Hofbauer cells. (G) CD68- and HBIG-double-positive immunohistochemical staining. Black arrow: HBIG in Hofbauer cells. (H) Comparison of HBIG intensity between the groups.