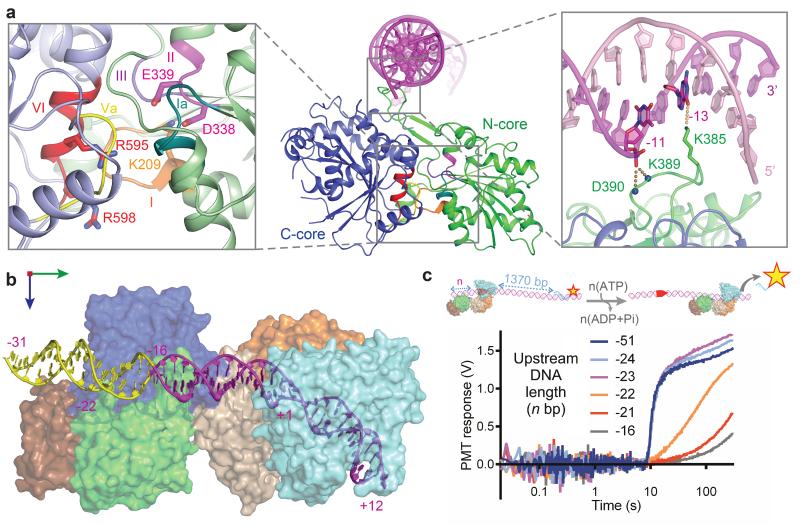
Figure 3. Architecture and upstream positioning of the ATPase domains.
a, ATPase architecture highlighting: (left inset) conserved SF2 helicase-like motifs, with ATP-interacting residues as sticks; (Right inset) DNA interaction of loop S383-D390, with side-chain of K385 as sticks and main chain nitrogens of K389 and D390 as spheres. b, Model of nuclease-ATPase interactions with an extended DNA (in yellow). c, The effect of upstream DNA length on triplex displacement. (cartoon) LlaGI motor activity initiated with ATP was monitored on DNA with varying upstream DNA.