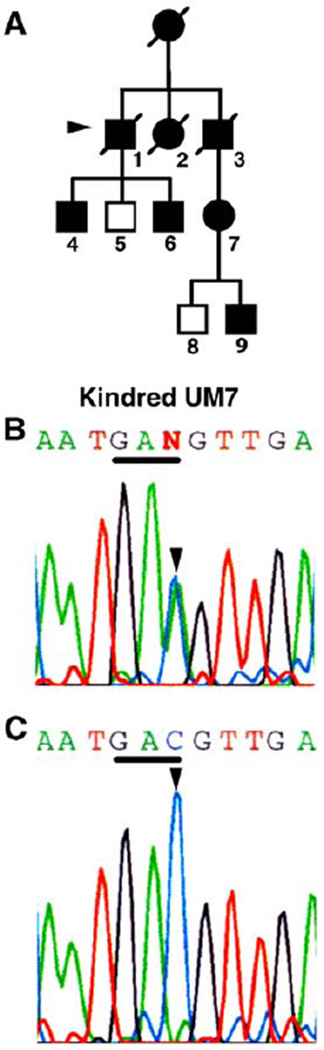
Fig. 2.
Mutations in one kindred with slow-channel syndrome affect a β subunit residues. (A) Pedigree of kindred UM7. Proband 7-1 (arrowhead), his sons, 7-4, 7-6, and niece 7-7 had abnormal electrodiagnostic studies. (B) Genomic sequence of the β subunit encoding the region of the M1 domain complementary strand, nucleotides 765– 775, containing the nucleotide position affected in kindred 7. The colored single-letter codes above show the letter N at position 770, where the sequence indicates two nucleotides. Shown is sequence from patient 7-6. One of the parental strands contains a C-to-A (antisense of G-to-T, arrowhead) substitution, which is present in equivalent abundance to the normal C and which alters the codon GTC to TTC. This mutation occurs at codon V229 and predicts a substitution of a phenylalanine residue. The complementary sequence of codon 229 is underlined. The larger black letters are letter codes for the corresponding amino acids and indicate the position encoding the wild type, valine (V), together with the mutant phenylalanine (F), read in the reverse sequence of the complementary strand. (C) Sequence of the same region obtained from the patient’s normal cousin (7–8) containing only a nucleotide C and amino acid valine at this position.