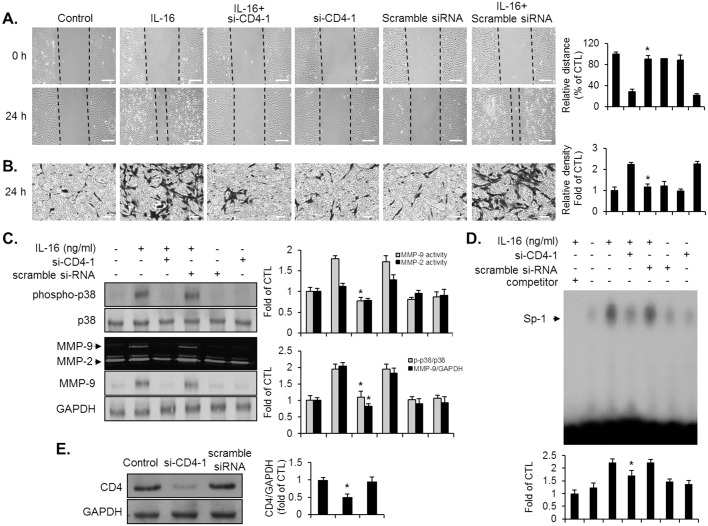
Fig 5. Effect of si-CD4-1 on IL-16-induced promotion of migration, invasion, p38MAPK phosphorylation, MMP-9 expression, and Sp-1 binding activity in VSMCs.
Cells were transfected with either si-CD4-1 or scramble siRNA, then followed by stimulation of IL-16 for 24 h. (A, B) Indicated cells were subjected to wound-healing assay and invasion assay. Scale bars represent 400 μm (wound-healing) and 100 μm (invasion). *P < 0.01 compared with IL-16 treatment. (C) Zymography and immunoblot was used to determine the MMP-9 expression using cell supernatants and cell lysates. For the phsosphorylation of p38MAPK, transfected cells were incubated for 10 min, and then the cell lysates were analyzed via immunoblot. *P < 0.01 compared with IL-16 treatment. (D) After transfection of either si-CD4-1 or scramble siRNA, indicated cells were cultured with IL-16 (50 ng/ml) for 24 h. Binding activity of the Sp-1 motif was examined by EMSA from nuclear extracts using radiolabeled oligonucleotide probes. Unlabeled Sp-1 (1 picomole) was used as a competitor control. *P < 0.01 compared with IL-16 treatment. (E) The efficacy of silencing gene of CD4 in VSMCs. Cells were transfected with either si-CD4-1 or scramble siRNA. The protein level of CD4 was evaluated by immunoblot. GADPH was used as an internal control. Results are reported as the means ± SE from three triplicate experiments. *P < 0.01 compared with control.