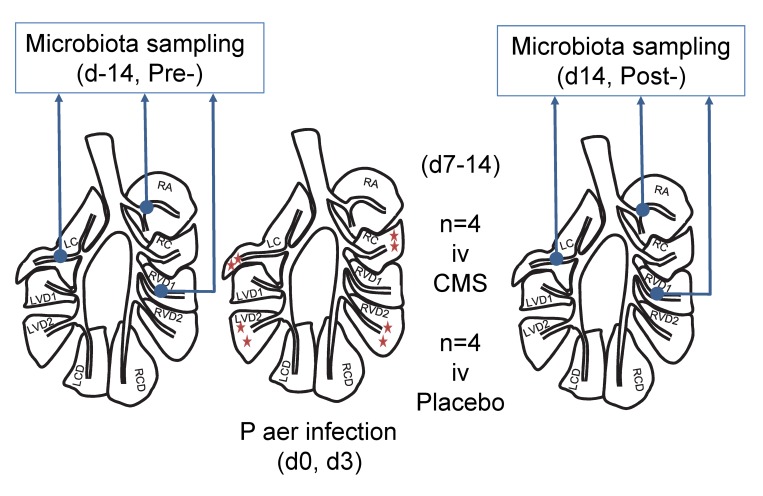
Fig 1. Microbiota sampling protocol.
During a baseline examination lung health was confirmed in the form of direct visualisation of the airway tree and later cytological analysis of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF). Protected specimen brush (PSB) samples were collected from the segmental bronchus serving the right apical (RA) lobe, the first ventral diaphragmatic (RVD1) segment of the right caudal diaphragmatic lobe, and the left cardiac (LC) segment of the apicocardiac lobe (Pre-samples). BALF was subsequently collected from RA. At least two weeks later P. aeruginosa agar beads were instilled into the right cardiac (RC) lobe, the second ventral diaphragmatic (RVD2) segment of the right caudal diaphragmatic lobe, the left cardiac (LC) segment of the apicocardiac lobe, and the second ventral diaphragmatic (LVD2) segment of the left caudal diaphragmatic lobe. Three days later these instillations were repeated. Four days after the second instillation sheep were randomly assigned to daily intravenous injections of either CMS or placebo. Eleven days after the second instillation–after one week of daily injections—PSB specimens were obtained from the previously sampled lobes (RA, RVD1 and LC) (Post-samples). After the sheep was killed and the lungs removed for further analysis, BALF was derived from each segment under study (RA, RC, RVD1, RVD2, LC and LVD2) prior to further dissection, sampling and recording.