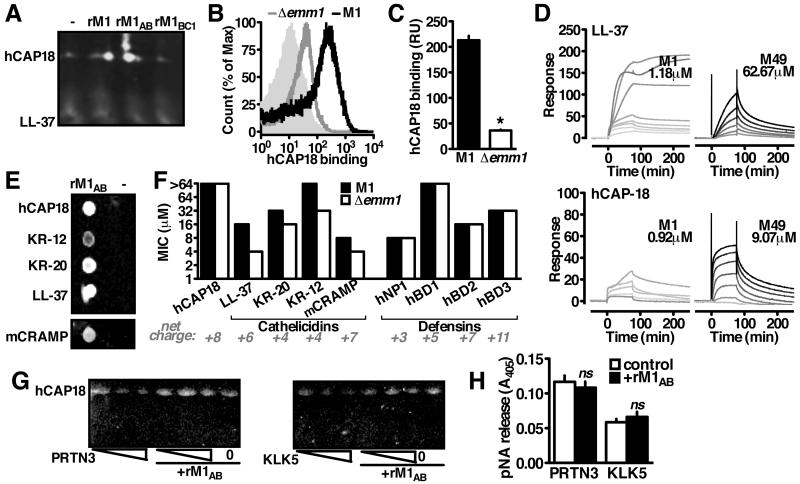
Figure 2. M1 Binds Immature Cathelicidin to Block Antimicrobial Peptide Generation.
(A) Interaction between rM1 and cathelicidin from neutrophil lysate by pulldown analysis and Western blot using anti-LL-37 antibody. (B, C) FACS detection of recombinant hCAP18 on the bacterial surface with anti-LL-37 antibody indicates Δemm1 GAS binds significantly less hCAP18 than wild-type GAS. (D) Representative sensorgrams from surface plasmon resonance analysis of M1 or M49 protein binding to immobilized LL-37 or hCAP18. Greyscale indicates concentration of M protein analyte in two-fold dilutions starting from 80 M (black) to 78.125 nM (lightest grey), starting from 5 μM (M1-LL-37), 80 μM (M49-LL-37), 1.25 μM (M1-hCAP18), or (D) 80 μM (M49-hCAP18). (E) Pulldown analysis with rM1 as bait for full-length (hCAP18) or truncated (LL-37, KR-20, KR-12, mCRAMP) forms as shown by dot blot probed with anti-LL-37 antibody (B). (F) Resistance of wild-type and Δemm1 GAS to full-length cathelicidin and the antimicrobial peptides from the cathelicidin (LL-37, KR-20, KR-12, mCRAMP) and defensin (hNP1, hBD1, hBD2, hBD3) families. (G) Cleavage of recombinant hCAP18 by increasing amounts of proteinase-3 (PRTN3) or kalikrein-5 (KLK5) (1, 2, 5 enzymatic units) in the presence or absence of rM1, as visualized by Western blot with anti-LL-37 antibody. (H) Enzymatic activity of proteinase-3 or kalikrein-5 in the presence of rM1. Figures are representative of at least 3 independent experiments.