Fig. 5.
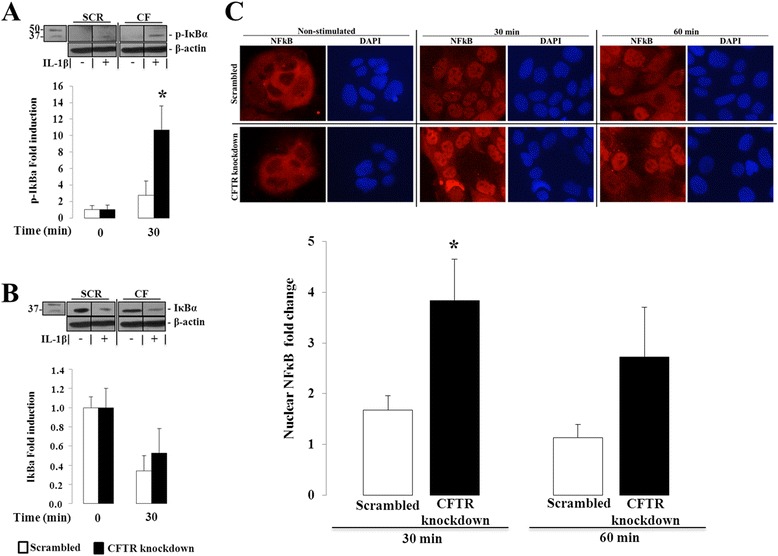
Effect of CFTR knockdown on IκB phosphorylation and NF-κBp65 nuclear translocation in Caco-2/15 cells. Cells were incubated from 0 to 60 min with 25 ng/mL of IL1-β. (a) Protein expression of phosphorylated IκB and (b) total IκB was analyzed by Western blotting. Data represent the means ± SEM of n = 4 independent experiments and both protein expressions were normalized to β-actin and reported as fold induction over basal expression. Western blot images are representative of the results obtained in the four independent cell culture experiments. (c) Ratio of nuclear to cytoplasmic fluorescence intensity of NF-κBp65 was calculated following the quantitative analysis of digitized immunofluorescence images. Data represent the means ± SEM of n = 5 independent experiments. Data are reported as fold induction over basal ratio of nuclear to cytoplasmic fluorescence intensity of NF-κB p65 after a 30 and 60 min-incubation with 25 ng/ml of IL1-β. Immunofluorescence images representing NF-κBp65 nuclear and cytoplasmic fluorescence intensity (in red) and DAPI nuclear staining (in blue) from scrambled and CFTR knockdown cells after 0, 30 and 60 min of IL1-β stimulation. Contrast and luminosity were standardised for all images. *p < 0.05 vs. scrambled-infected cells
