Fig. 3.
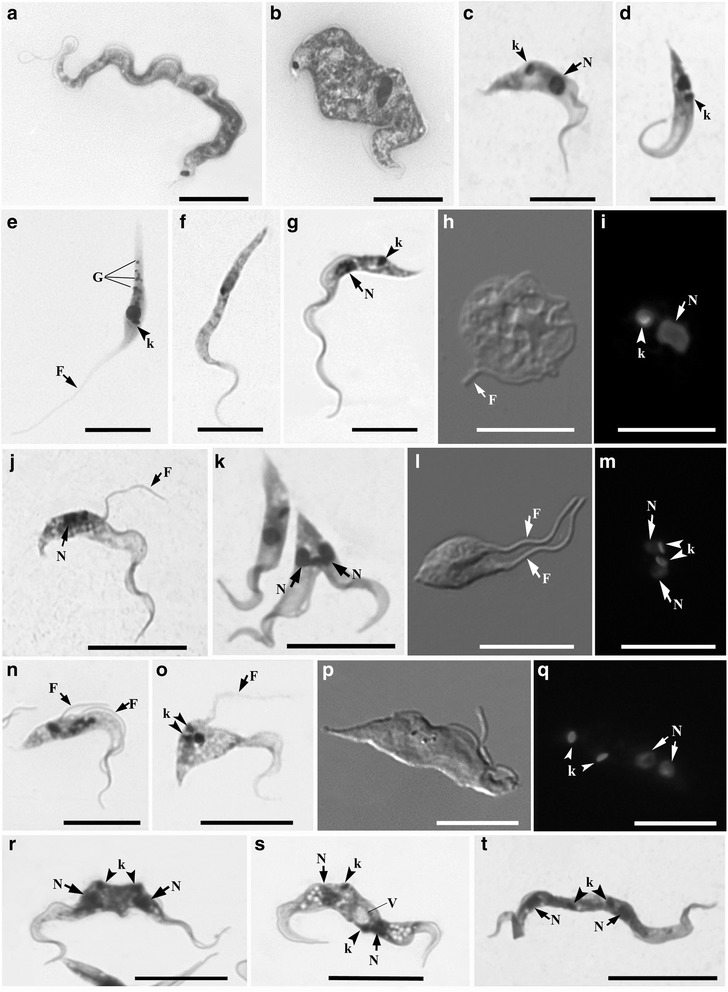
Light microscopy analysis of Trypanosoma abeli n. sp. cultured in vitro. Parasites were visualized by Giemsa staining (a-g, j, k, n, o, r-t), differential interference contrast (h, l, and p), and fluorescence microscopy using Hoechst H33342 (i, m, and q). Elongated (a) and short and broad (b) bloodstream trypomastigotes. Short trypomastigotes (c) and ‘pyriform’ (i.e. “pear shaped”) epimastigotes (d and e) and were the first developmental forms observed in primary cultures. Although trypomastigotes (g) were again observed in stationary phase, as well as spheromastigotes (h and i), with a round kinetoplast (arrowhead in i) and short flagellum (arrow in h). Cultures contained dividing epimastigotes (j-m) and trypomastigotes (n-t) at different stages of cell division, with duplicated single-copy structures, including the flagellum (F), the nucleus (N) and the kinetoplast (k). G, granules; V, vacuoles. Scale bar, 10 μm
