Fig. 2.
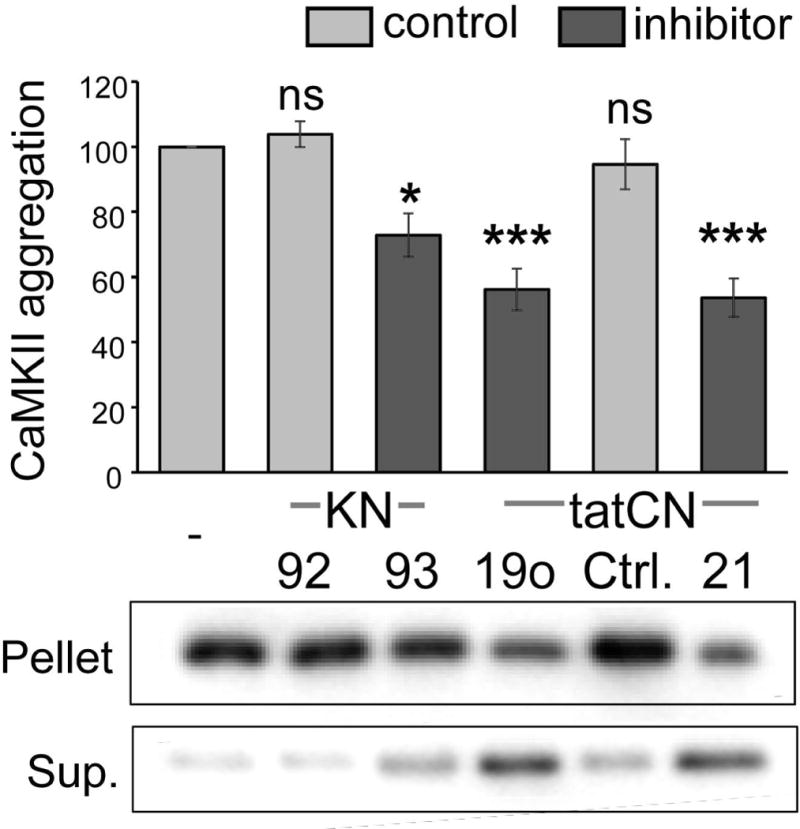
CaMKII aggregation in vitro is reduced by the CaMKII inhibitors KN93, tatCN19o and tatCN21. CaMKII aggregation was induced at pH 6.5–6.8 by the addition of 1 mM ADP in the presence of Ca2+/CaM and 10 μM KN93, KN92, 5 μM tatCN19o, tatCtrl, or tatCN21, as indicated (with 10 μM KN compounds or 5 μM tat peptides). Aggregates were separated by centrifugation from soluble kinase, and both pellet and supernatant (Sup.) were analyzed for CaMKII content by Western blot. Aggregation was normalized to ADP-only control. CaMKII inhibitor (dark grey) versus control substance (light grey) conditions are indicated. One-Way ANOVA with post-hoc Tukey’s test indicated that the inhibitors KN93, tatCN19o and tatCN21 significantly reduced aggregation (* p<0.05, *** p<0.001, ns = non-significant as compared to ADP-only control; n=5–6).
