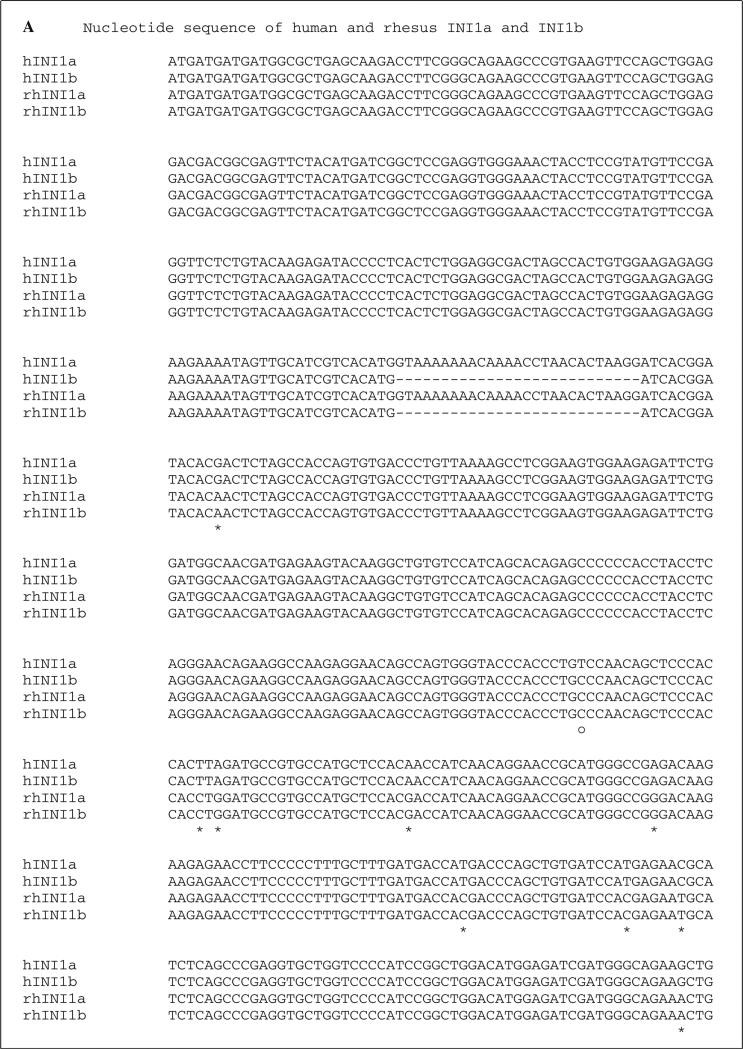
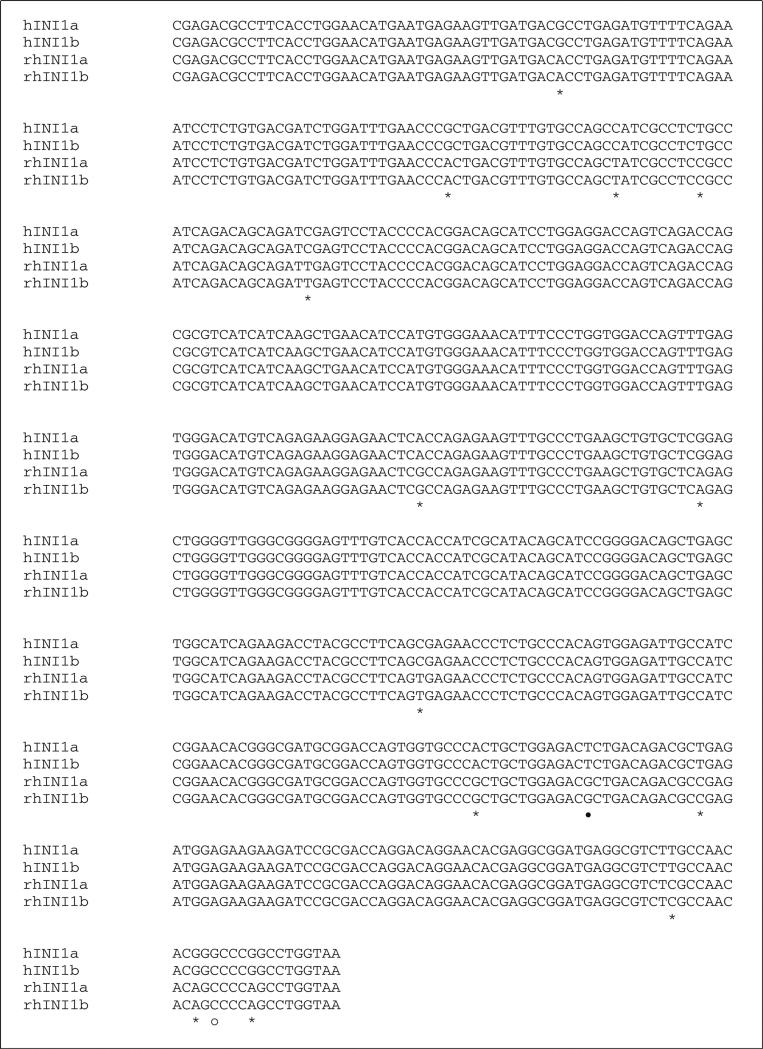
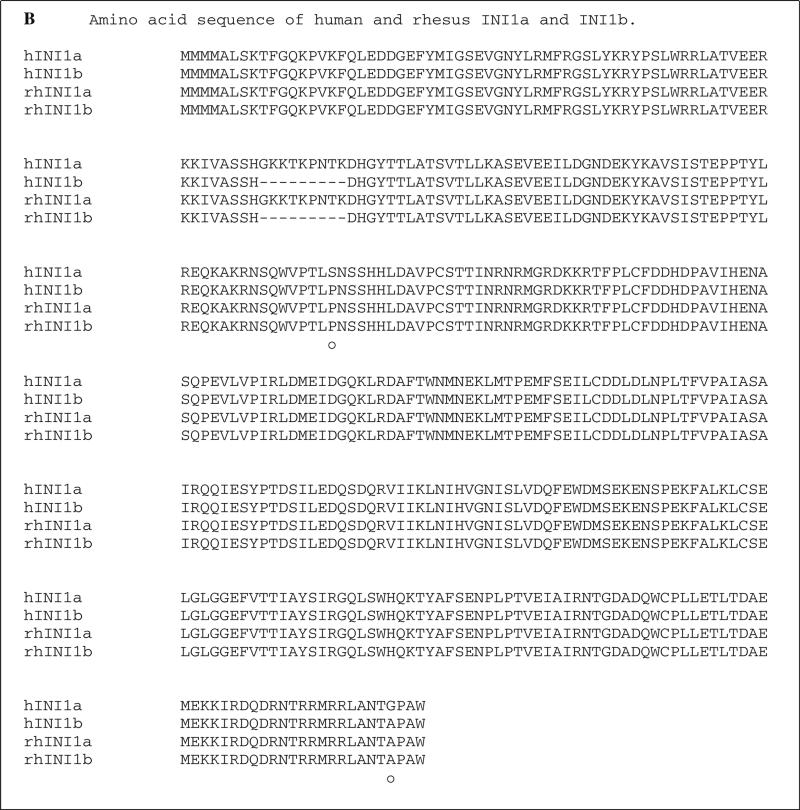
Fig. 1.
Sequence alignment of human and simian INI1. A. DNA sequence alignment. Sequences of hINI1a and hINI1b were retrieved from GenBank (accession numbers U04847.1 and AB017523.1, respectively. “—” indicates an in-frame deletion in the nucleotide sequence of INI1b produced by alternative splicing. Twenty-three single nucleotide differences were identified by alignment, and of those, 21 (91 %) were transitions (*) and two (9 %) were transversions (•). differences in the nucleotide sequences of human INI1a and INI1b are indicated by “○”. B. Amino acid sequence alignment. All of the substitutions are silent mutations. However, two substitution mutations identified between human INI1a and INI1b resulted in amino acid changes, as indicated by “•”. “—” indicates the amino acid deletion in both human and simian INI1b due to the in-frame deletion of nucleotide sequences