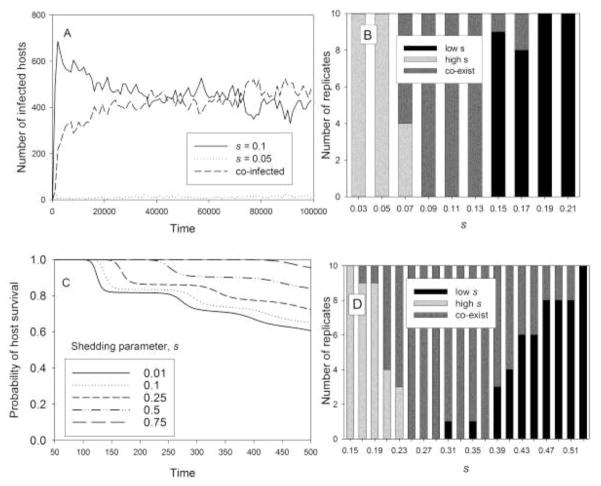
Fig. 4.
Competition and coexistence for a low-mortality pathogen. Within-host dynamics follow the virus model of Eqs. (4). Simulations as in Fig. 3 except that here m(V) = 10−14V, allowing hosts to survive longer. A. Clones with s = 0.05 day−1 and s = 0.1 day−1 coexist, with the former at low density while the latter clone and co-infected hosts are at higher densities. B. Number of replicates (out of 10) for which the higher-s clone eliminated the lower-s clone (high s), the reverse (low s) and the two clones coexisted (coexist) at 50,000 days. The abscissa is labeled with the average s of the two competing clones, which were separated by 0.02 units. C. Probability of host survival with m(V) = 10−14V, with virus model and other parameters as in Fig. 1B. D. Same as B, except θ = 10−16 and simulations were run for 100,000 time units.