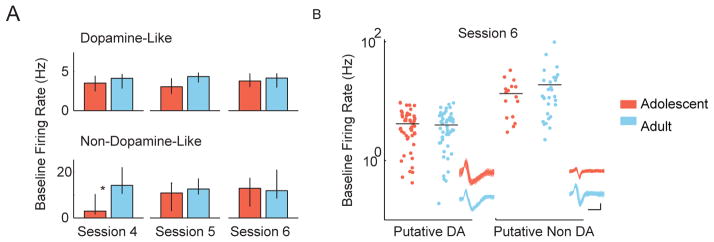
Figure 3.
Adolescent and adult VTA neurons have similar activity levels. (A) The baseline firing rates of dopamine-like and non-dopamine-like neurons in adolescent and adult rats are displayed for sessions 4–6. Baseline firing rates were non-normally distributed, and accordingly, firing rates are depicted as median ± 95% CI. (B) The full distributions of baseline firing rates of dopamine-like neurons and non-dopamine-like neurons in session 6 are plotted on a log axis. VTA units were classified as dopamine-like neurons if they had low baseline firing rates (< 10 Hz) and wide spike waveforms (> 1.2 ms). Each dot represents one unit. One hundred example spike waveforms from one unit in each group are shown in the lower right (scale bar x axis = 0.5 ms, y axis = 0.1mv).