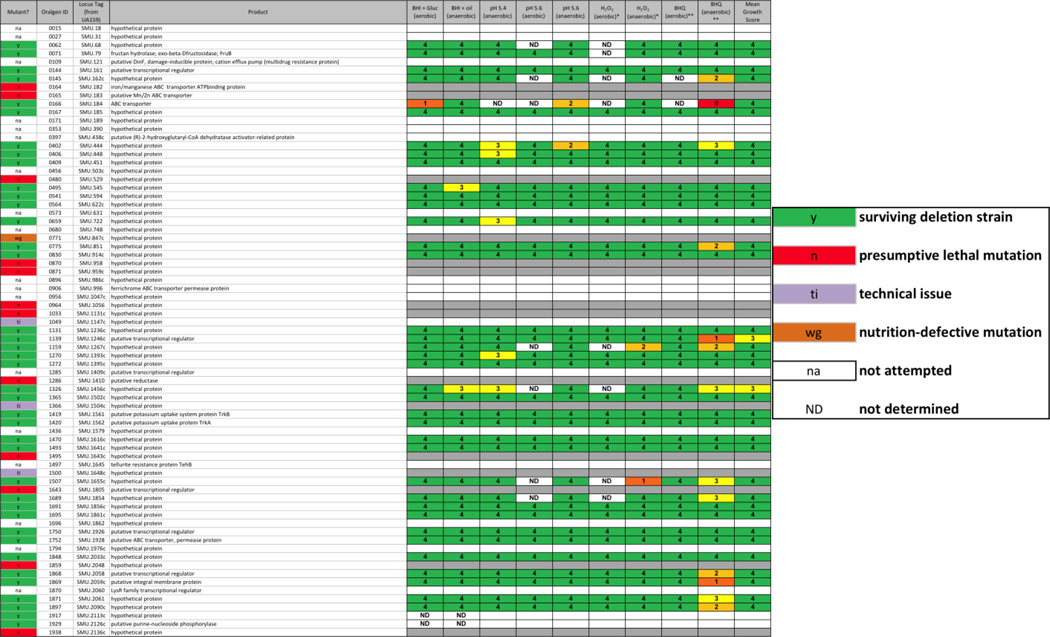
TABLE 2. Unique core gene from S. mutans identified in the deletion strain collection.
In a study by Cornejo, et al., 73 genes were identified from a core S. mutans genome that had been annotated as encoding conserved hypothetical proteins (Cornejo, et al. 2013). Table 2 contains these 73 genes and the results from our deletion mutant study. In the far left column, red (n) cells indicate a putative lethal mutation, green (y) cells indicate successful mutation, purple (ti) cells indicate a technical issue that precluded the making of a deletion strain, orange (wg) cells indicate that resulting transformants were unable to grow in liquid medium for the preparation of a frozen stock, and white (na) cells indicate that the construct was not attempted due to inability of our primer calling algorithm to design primers for the deletion construct. Scoring for each physiological screen was performed as described in METHODS, on a scale from 0 – 5; ND = not determined.