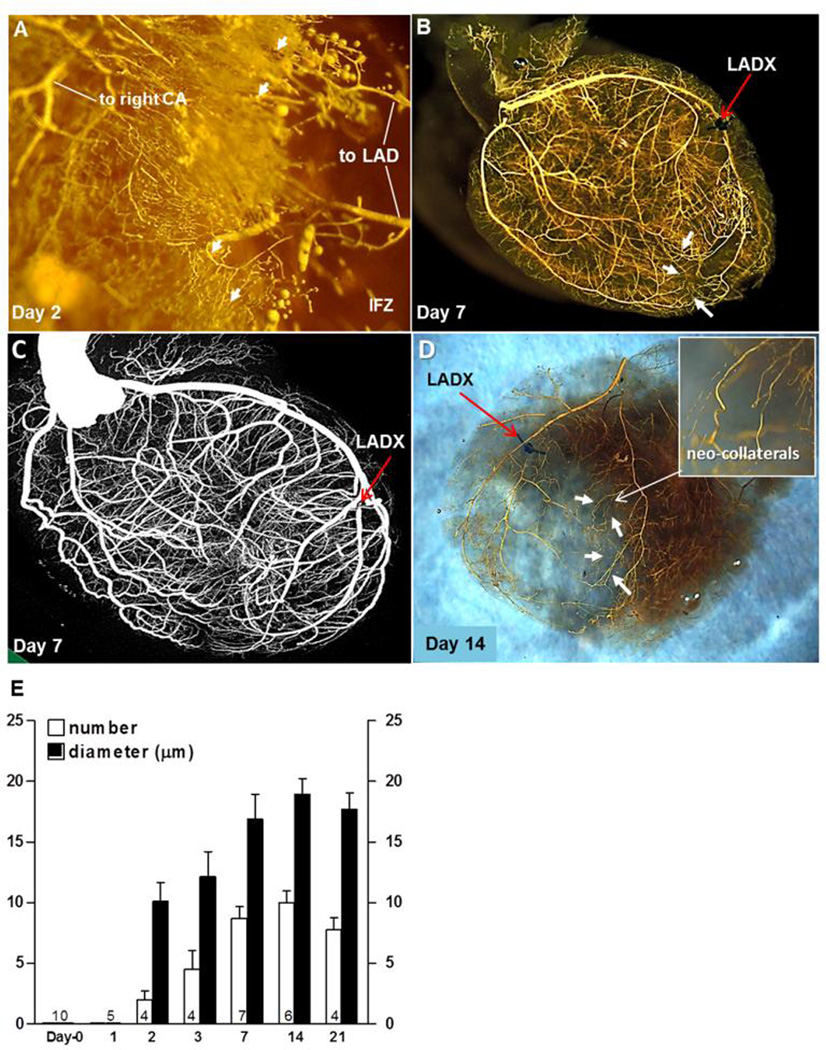
Figure 2. New collaterals rapidly form in mice after ligation of the distal LAD tree (LADX).
The “neo-collaterals “ cross-connect the LAD tree to the right coronary (CA) and septal artery trees. Same methods as in Figure 1 were used. A, Neo-collaterals (arrows) provide partial back-filling of LAD tree 2 days after LADX. IFZ, infarct zone. B, Arrows are several superficial neo-collaterals to right coronary artery tree; neo-collaterals on day-7 provide complete back-filling of LAD tree (See also Online Figures 10,12). C, Micro-CT imaging with Scanco40 at maximal resolution shows complete back-filling but is unable to resolve neo-collaterals. D, Epicardial neo-collaterals (arrows) after removal of the underlying myocardium and opposite LV wall to aid imaging. E, Time-course for neo-collateral formation after LADX in C57BL/6 mice; number (n) of mice given at base of bars in this and subsequent figures. Maximal number and average diameter of the neo-collaterals are achieved by 7 days.