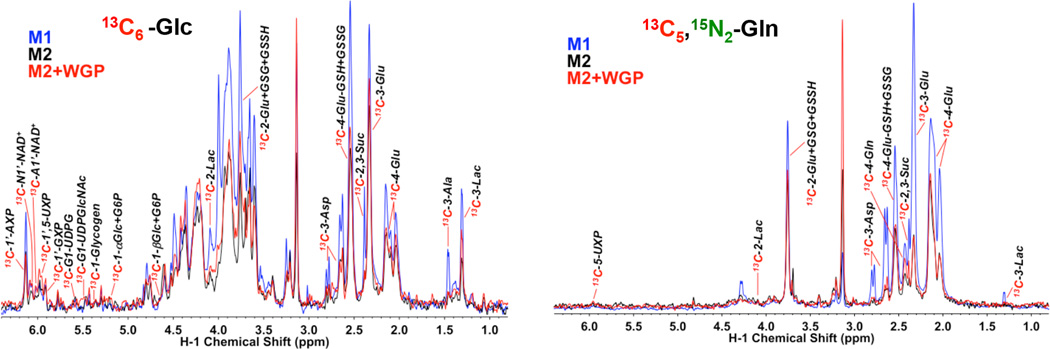
Figure 2. M1 and WGP β-glucan activated M2 BMM display elevated 13C incorporation into glycolytic and Krebs cycle metabolites from labeled Glc and Gln.
M1, M2, or WGP-treated M2 BMM extracts were analyzed by 1D 1H{13C} HSQC NMR as described in the Materials and Methods. The HSQC analysis compared the peak intensity of protons attached to 13C atoms (akin to 13C abundance) at specific positions of various metabolites. Compared to M2 BMM, M1 BMM exhibited elevated activity of glycolysis, Krebs cycle, glutathione synthesis, and nucleotide synthesis, as evidenced respectively by the increased 13C abundance of cellular lactate (Lac; cf. also Figure 3 for medium lactate), Asp/Glu/succinate (Suc), adenine nucleotides (AXP), and glutathione (GSH)/glutathione disulfide (GSSG) derived from these pathways using Glc or Gln as precursor (cf. Figure S2). WGP-treated M2 macrophages also displayed elevated activity of glycolysis and Krebs cycle over untreated M2 macrophages but not in nucleotide and glutathione biosynthesis. 1’-AXP, -GXP, and -UXP: 1’-ribose of adenine, guanine, and uracil nucleotides, respectively.