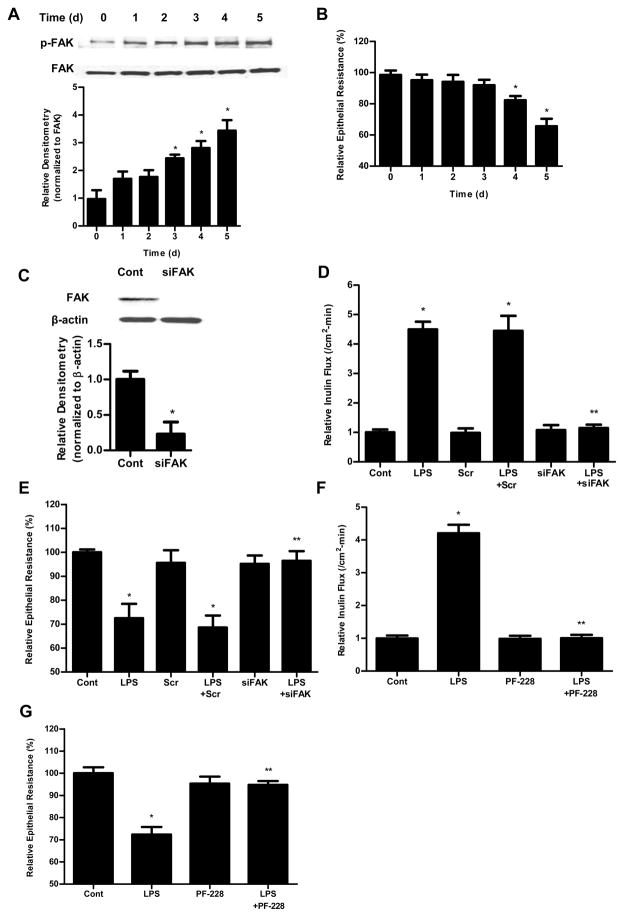
Figure 1.
The involvement of FAK in LPS-induced increase in Caco-2 permeability. (A). Time-course effect of LPS (0.3 ng/ml) on phospho-FAK in Caco-2 monolayers. The densitometry analysis indicates relative levels of phospho-FAK reveled time dependent significant increase. (B). Time-course effect of LPS (0.3 ng/ml) on Caco-2 TER. The effect of LPS (0.3 ng/ml) on Caco-2 TER was measured over a 5-day experimental period. The mean TER for control Caco-2 monolayers was 512 ± 15 Ω • cm2. (C). The siRNA FAK transfection resulted in a near-complete depletion of FAK expression as assessed by Western blot analysis and Densitometry analysis. The Western blot analysis was performed 72 h after siRNA FAK transfection. (D). The siRNA-induced silencing of FAK prevented LPS-induced increase in Caco-2 inulin flux. (E). The siRNA-induced silencing of FAK prevented LPS-induced drop in TER in Caco-2 monolayers. The mean TER for control Caco-2 monolayers was 520 ± 6 Ω • cm2. Inhibition of FAK function by inhibitor PF-228 prevented LPS-induced increase in Caco-2 inulin flux (F) and drop in TER (G). The mean TER for control Caco-2 monolayers was 485 ± 13 Ω • cm2. n=4. *, p<0.0001 vs control. **, p<0.0001 vs LPS treatment.