Figure 3. Increased turnover rate of lung IM correlates with increased blood monocyte turnover in SIV-infected macaques.
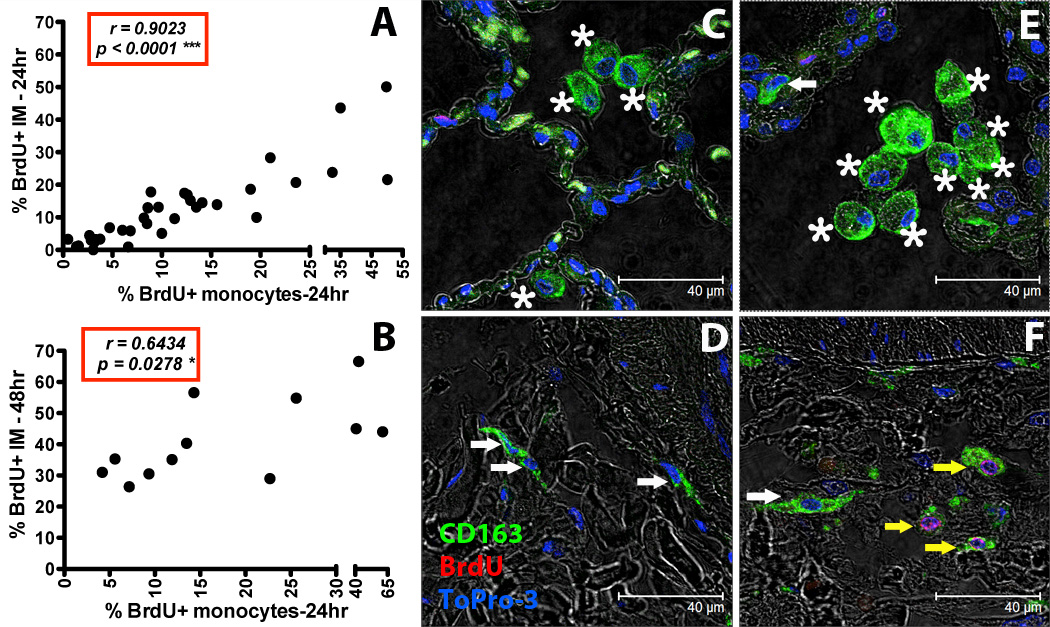
BrdU or EdU was injected i.v. into SIV-infected or uninfected rhesus macaques and lung IM were analyzed by flow cytometry (A and B). By Spearman’s correlation analyses, a significant correlation was observed between blood monocyte turnover and IM turnover 24 hr (A: n = 35) or 48hr (B: n = 12) after BrdU/EdU injection. Paraffin-embedded lung tissue sections obtained after necropsy from uninfected (C and D: representative of 4 animals) and SIV-infected rhesus macaques (E and F: representative of 4 animals) were stained with anti-CD163 antibody (macrophages-Green), anti-BrdU antibody (turnover-Red) and Topro-3 (nucleic acid-Blue). Images were captured with a Leica TCS SP2 confocal microscope equipped with a 3-laser (Leica Microsystems) under an oil objective (63×, fluotar/NA 1.0) for a final magnification of 1260×. White arrows indicate CD163-staining IM cells (green), yellow arrows indicate CD163-staining IM cells that incorporated BrdU (green and red), and asterisks indicate CD163-staining AM (green).
